What is the competence of a thoracic surgeon?
Thoracic surgeon deals with organ surgery chest: breast, surgery of the lungs, heart, esophagus, mediastinum.What diseases does a Thoracic surgeon deal with?
- Diseases of the mediastinum (mediastinitis, mediastinal cysts, mediastinal tumors);- Diseases of the thymus gland;
- Purulent diseases and neoplasms of the lungs;
- Diseases of the esophagus (esophagitis, reflux esophagitis, ulcers, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux, achalasia, spastic disorders, scleroderma);
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
What organs does a thoracic surgeon deal with?
Larynx, pharynx, esophagus, trachea, lungs, thymus gland (thymus), thyroid and parathyroid glands, diaphragm, liver, stomach, heart, pericardium, large blood and lymphatic vessels.When should you contact a Thoracic Surgeon?
Esophageal symptoms include:Heartburn;
- Belching;
- Dysphagia - disruption of the passage of food through the esophagus (see above);
- Feeling of a lump behind the sternum;
- Odynophagia - pain when food passes through the esophagus;
- Pain in the epigastrium (“under the stomach”) and esophagus;
- Hiccups, vomiting.
In addition, this radiography allows early detection areas of atelectasis and the formation of alveolar foci. These findings are inevitably correlated with clinical findings, especially auscultation, before deciding whether fibroaspiration is desirable.
For partial excisions, the first drain is removed on average on the 3rd postoperative day, and the next one after 48 hours. After removal of the drain, radiographic guidance is systematically performed. For pneumonectomies, only one drain is used; it is not absorbed. Existing drainage systems can maintain "intracavitary pressure" to avoid mediastinal movements. The drain is usually removed after 48 hours. In some cases, subcutaneous emphysema may occur, often caused by coughing. This emphysema in the early period is associated with severe removal of intracavitary air in the subcutaneous tissues.
Thymus cancer, symptoms:
There are no clinical manifestations of thymus cancer in the early stages. When the tumor spreads to neighboring organs, respiratory distress, difficulty in the outflow of blood from the superior vena cava and its tributaries (cyanosis, swelling of the face and upper limbs, increased intracranial pressure, headaches), heart rhythm disturbances.
Progressive filling of the cavity is monitored by daily radiography. Some teams do not use drainage. In these cases, it is sometimes necessary to blow air into the cavity to compensate for excessive mediastinal deviation on the controlled side. Conversely, filling a cavity too quickly and too important may require evacuation of the puncture.
Thoracic surgery is a painful surgery due to the approach, side slope during the procedure and the presence of pleural drains. Pain is assessed using a visual analogue scale. This allows pain intensity to be assessed several times a day in order to tailor analgesia as much as possible. Several methods of pain relief are used: self-controlled morphine intravenous analgesia, thoracic epidural analgesia, which allows the introduction of associations of local anesthetics and opioids into the epidural space.
With metastatic changes in the bones, severe pain syndrome is possible. In the case of secondary tumor damage to the brain, focal neurological symptoms develop.
What are the main types of diagnostics usually performed by a thoracic surgeon?
- Thoracoscopy;- Thoracoscopic resection of focal lung diseases localized by preoperative contrast;
- Video thoracoscopic pleurodesis in the treatment of malignant exudative pleurisy;
- Intraoperative ultrasound examination during thoracoscopic procedures for focal lung diseases;
- Videothoracoscopy for primary diseases of the mediastinal organs;
- Video thoracoscopic thymectomy;
- Arthroscopy;
- Laparoscopy;
- Hysteroscopy;
- Biopsy. First aid for chest and lung injuries.
In case of chest injuries, the victim is worried severe pain, preventing you from breathing fully.
The quality of analgesia is critical because, in addition to the patient's comfort, it significantly improves the patient's functional performance and ability to actively participate in physical therapy after surgery. Physiotherapy is provided by a dedicated physiotherapist with a minimum of two sessions per day; Its purpose is to avoid bronchial congestion by facilitating drainage and expectoration of bronchial secretions. The patient is encouraged to continue these retrainings independently using the stimulus material.
Food begins the next day, gradually. Only patients who have undergone pneumonectomy or resection with recurrent nerve victim resume feeding according to a strict protocol. Usually the water is replaced with gel water. The first catch is made in the presence of a guardian to check that there are no false roads to avoid aspirations.
First aid:
1. Make the victim sit comfortably.
2. Apply cold to the damaged area.
3. You can apply (while inhaling!) a tight bandage made of a bandage or towel to the chest.
4. If there is a wound, it is necessary to treat its edges with iodine solution and cover with a clean bandage. With a penetrating wound to the chest, a whistling sound is heard in the wound area when inhaling and exhaling. Along with the escaping air, bloody fluid and blood clots fly out of the wound. To such a wound, polyethylene or other airtight material should be attached with strips of adhesive tape (one on top of the other, like a tile) or secured with a bandage.
5. Deliver the victim to a medical facility as soon as possible in a sitting or semi-sitting position.
The length of postoperative stay is about 8-10 days. Rehabilitation of the respiratory tract continues at home or in a specialized center, as well as pain management and prevention of thromboembolic risks. The first postoperative consultation takes place during the 3rd or 4th week. In addition to the clinical examination, a chest x-ray is systematically performed. This x-ray can be used to check the ideal expansion of the lung or the filling level of the pneumonectomy cavity.
Promotions and special offers
Medical news
24.11.2017
Specialists from the Institute of Surgery named after. A.V. Vishnevsky performed an endoscopic coronary artery bypass surgery on a patient in whom two of the three arteries of the heart were blocked, that is, turned off from the bloodstream. There are still such sick people in our country...
Pulmonary Oncology Surgery offers wide range interventions, the choice of which depends on an accurate assessment of the tumor status and patient function. Technical proficiency in these interventions is fundamental to ensuring both the quality of prompt follow-up and improved oncologic outcomes. This control can only be obtained from a minimum threshold of activity. In addition, preoperative assessment of patients as well as postoperative monitoring require an optimal medical and technical environment.
08.11.2017
Scientists from the University of Colorado in the US have forced cancer cells to be more susceptible to drugs. Affected cells need...
14.08.2017
Employees at West Virginia University experimentally came to the conclusion that the use of electronic evaporators leads to premature aging blood vessels and heart.
There are two types of tumors: "small cell" carcinoma and "non-small cell" carcinoma. The latter, the most common, is usually treated with surgery if advancement allows. A quarter of non-small cell carcinomas are at the surgical stage when they are discovered. Surgical treatment will be sufficient for 15-20% of them.
It is a common cancer as it is the most common cancer in humans. Smoking is a major risk factor. Pollution, radon and asbestos, linked to genetic factors, may also be a cause. Lung cancer treatment is a complex approach that requires individualized management. Possible treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery.
05.07.2017
Australian scientists have discovered that at low temperatures, ultraviolet light contributes to the accumulation of DNA damage. Experts made this conclusion after observing...
02.06.2017
By 2021, a pharmaceutical plant will be built in the city of Pushkin, which will be able to produce 18 types of drugs and chemical substances.
Non-small cell cancers
Small cell cancers, depending on their size, progression and location, are treated surgically. Our two lungs are divided into lobes, and each lobe is divided into segments. The surgical procedure involves removing the focal point of the tumor. Depending on its volume, lobectomy, segmentectomy or pneumoectomy will be performed. Lymph node dissection completes the surgical procedures.
Small cell cancer
Surgical treatment for small cells is rare. The limited extent of the tumor and its location in the peripheral areas of the lung are the main criteria for its possible use. The right and left lungs are located in the chest, on either side of the heart, right lung has three lobes while the left lung has two and the lungs are surrounded by a membrane.
Medical articles
Many pregnant women do not realize that cosmetics, or rather some of its components, can have a detrimental effect on the unborn child.
The symptoms of hay fever are very similar to colds and flu. A state of general malaise, nasal congestion with constant discharge, pain and itching in the eyes, cough, heavy breathing - all these or some of the presented symptoms are very worrying for patients with hay fever.
Pulmonary intervention may be required for a number of reasons, usually lung cancer, the leading cause of cancer deaths in Belgium. It can also be metastases in the lungs, which arise from a previously treated tumor located in another organ of the body. It may also be a persistent inflammatory process or a benign abnormality. Surgical removal of the tumor offers the best chance of survival for early stage lung tumors. The classic method of tumor ablation is a turotomy, which is a large incision between the ribs on the side of the chest to reach the lung.
According to statistics, every fourth resident of Europe and Russia has joint pathology. Rheumatic diseases affect people of any age and gender. There are about 200 different rheumatic diseases: from different options arthritis to osteoporosis and systemic connective tissue diseases.
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is one of the most aggressive and deadly forms of breast cancer. It is quite difficult to detect, it grows quickly and metastasizes. In addition, among the chemotherapy drugs currently used, the main drugs for treating TNBC are so toxic that patients often cannot tolerate treatment. However, scientists see a solution to the problem in cruciferous vegetables. Yes, back in them.
Three small incisions are made; an endoscope connected to a video camera is inserted through one of these incisions, and instruments are inserted through the other incisions. Images are projected in high definition on the TV screen. With these images, the surgeon can visualize the lungs and other structures in the chest, allowing the lobe of the blade to appear with lymph nodes in and near the lobe. When the petal is closed, the slits are closed and one or two small tubes are left in place to remove excess fluid and air from the outside.
These chest drainage holes are removed a few days after surgery. Patients with early stage lung cancer who have small tumors and have not spread to tumors outside the lung are good candidates for this method. In patients with tumors that are large or centrally located, involving large airways or lymph nodes in the middle of the chest, a traditional thoracotomy is often more appropriate.
The area of medicine in which a thoracic surgeon specializes is called thoracic surgery, and deals with the treatment of diseases of the chest organs - lungs, esophagus, bronchi, trachea, pleura. How to get an appointment with this specialist, what diagnostic and surgical methods he uses - questions that will be discussed in this article.
Less invasive than traditional thoracotomy.
- No opening of the ribs is required.
- Less pain.
- Faster recovery.
- Reduced risk of infections and bleeding.
From this brochure, we'd love to hear from you and let you know about it, and help you find your way around the world to learn about it. Bronchopleural fistula is a serious complication thoracic surgery with high mortality. Its diagnosis as early as possible is necessary. On the other hand, the subacute or chronic form presents a more difficult diagnostic challenge due to nonspecific symptoms; it requires antibiotic therapy tailored to the isolated microbes, effective drainage of the pleural space associated with complex surgical or endoscopic treatments that often need to be repeated.
What is thoracic surgery
The thorax is the region of the chest that includes the thoracic spine with the ribs extending from it, the chest wall, the diaphragm and top part abdominal cavity. The field of surgery dealt with by a thoracic surgeon covers a wide range of diseases of the chest organs - lungs, pleura, bronchi, trachea, esophagus. It includes providing assistance for injuries, acute conditions, pathologies, cancer and inflammatory processes.
Bronchopleural fistula is a rare but serious complication after pneumonectomy or surgical lobectomy. This article summarizes the incidence, etiology, and risk factors of fistulization. He is considering various therapeutic modalities, both surgical and endoscopic, to manage this complication.
The incidence varies depending on the etiology, surgical technique, and surgeon experience. It is also less common after surgery for benign conditions. Subacute and chronic forms, however, are very often associated with infection, both in immunocompromised patients and in patients with underlying medical conditions.
At modern diversity diagnostic methods, the thoracic surgeon has the opportunity to objectively evaluate clinical picture disease, choose the appropriate method of surgical treatment. There are the following main methods of thoracic surgery:
- thoracotomy;
- thoracoscopy;
- thoracentesis;
- puncture of the pleural cavity;
- drainage of the pleural cavity.
Thoracotomy
The central method of thoracic surgery is thoracotomy - opening the sternum using an incision in the intercostal tissue. It is performed in different areas, the location of the incision depends on the location of the disease and the objectives of the operation. There are median, anterolateral, posterolateral thoracotomy. During surgery, the patient lies on his back (during most open heart surgeries) or on his side (during lung resection). Minimal thoracotomy is the latest achievement of thoracic surgeons - the incision size does not exceed 10 cm.
Bronchopleural fistula: risk factors. Risk factors for bronchopleural fistula after pneumonectomy: stump size matters. Search for supported crayfish. If these benefits are generally recognized in abdominal, gynecological, cardiac surgery, otorhinolaryngology, they are not the same as for the pulmonary chest.
For this reason, according to experts, early diagnosis is of great importance in order to be able to intervene in the tumor when it is still small. Medical workers: Alloidio Antonella, Benvenuto Fulvio, Blanco Gianfranco, Andrea Denegri, Leoncini Giacomo, Novello Luca, Piras Maria Teresa, Risso Carlo, Taviani Mario.
Thoracoscopy
An endoscopic examination method, called thoracoscopy, allows the thoracic surgeon to conduct a broad diagnosis of the pleural cavity, the outer lining of the lungs, allowing for some types of micro-operations on the organs of the mediastinum, pleura, and lungs. Thoracoscopy is performed using a laparoscope, which is inserted into the pleural cavity along with a camera installed on it and a device for aspiration. Through it it is possible to take a biopsy, administer medicinal product, use of other surgical instruments.
Description of activity The group is responsible for the treatment of all surgical diseases of the chest, whether in elective or emergency situations. The structure has a predominantly oncological vocation. It operates within a multidisciplinary chest oncology team that meets weekly. Clinical cases are reviewed jointly by different specialists and a common therapeutic indication is given in accordance with current international guidelines.
Often, surgical therapy is integrated with other therapeutic regimens in a multimodal approach. In addition, the accessibility of the Institute of All Surgeries facilitates collaboration in the field of advanced cancer surgery. A patient who is receptive to surgical therapy is already in the preoperative therapy phase and is adequately prepared for surgery along a predetermined route. In addition to completing all preoperative surgical assessments, senior surgical candidates are assessed by a respiratory physiotherapist who teaches them how to perform a range of exercises at home and then in the perioperative phase.
Thoracoabdominal surgery
The field of surgery that involves caring for patients with diseases of the chest and organs located in the upper abdomen, such as the stomach or diaphragm, is called thoracoabdominal surgery. The relevant departments provide treatment:
- peritoneal tumors;
- emphysema;
- pulmonary hemorrhages;
- hernias of the chest wall, diaphragm;
- diseases of the esophagus;
- malformations of the mediastinum;
- chest wall injuries and their complications;
- damage to the trachea and bronchi.
Thoracic oncology
A surgeon who specializes in treating benign or malignant tumors in the chest cavity and upper peritoneum is called a thoracic oncologist. He is in charge of oncology, developing in:
- mammary glands;
- lungs;
- heart;
- esophagus;
- mediastinum;
- liver;
- stomach;
- thyroid and thymus glands.
What does a thoracic surgeon treat?
A thoracic surgeon provides assistance to patients suffering from various diseases of the thorax and its main organs. These may be conditions caused by trauma - hemothorax, pneumothorax and chylothorax (accumulation of blood, air and lymph in the pleural cavity), treatment of tumors of the chest organs, bronchial diseases, pneumonia, pathologies of the pleura or pericardium (tissue lining of the heart). A specialist in the field of thoracic surgery diagnoses and treats patients with the following diagnoses:
- pleurisy;
- lung abscess;
- pulmonary artery blockage;
- tracheal stenosis;
- accumulation of pus (empyema) in the pleural cavity;
- pulmonary atelectasis;
- inflammation of the costal bone tissue;
- bronchiectasis;
- pathologies of the esophagus, thyroid and thymus glands.
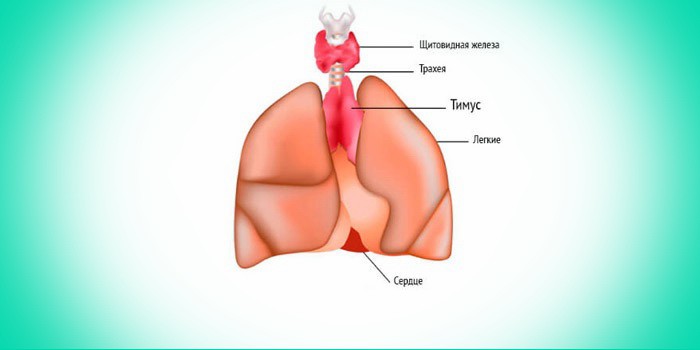
Thyroid and thymus gland
For the production of basic hormone regulators metabolic processes The thyroid gland is responsible. It is susceptible to open and closed mechanical damage, inflammatory diseases (thyroiditis), and can become a site for the development of a malignant tumor. A thoracic surgeon makes an accurate diagnosis and treatment (surgery) for cancer, cystic formations, nodular or toxic goiter of the gland.
The thymus gland or thymus, located in the center of the sternum, produces cells of the immune system, carries out lymphopoietic, endocrine and immunoregulatory functions. The state of the entire immune system of an adult and the development of all organ systems in a child depend on it. With an increase in size, hypofunction or hyperfunction of the gland and its other pathologies, autoimmune diseases develop, so timely examination by a doctor or surgeon specializing in diseases of the thorax is important.
Chest injuries
The following chest injuries are distinguished, in which victims are taken to the thoracic surgery department for emergency care:
- penetrating wound (gunshots, puncture wounds);
- industrial, road traffic injuries of a blunt nature;
- damage to the chest wall - fractures, bruises of the ribs;
- damage to mediastinal organs
The surgeon conducts a visual examination, percussion and auscultation of respiratory sounds, a complete examination of the body, and prescribes the necessary general and special laboratory tests. First aid includes ensuring free breathing (if foreign bodies get into the wound, they are removed as soon as possible to free the entire airway), relieving shock, and reducing pneumothorax tension. Further therapy is carried out according to the nature of the injury and the patient’s general medical history.
Respiratory diseases
A surgeon who deals with diseases of the lungs and other respiratory organs is a specialist highly qualified in this area of medicine. The subject of its activity is inflammatory processes, damage, congenital or acquired pathologies of the bronchi, trachea, and respiratory tract. If necessary, performs surgical intervention for tuberculosis or cancer of these organs.
Surgical treatment of esophageal pathologies
Surgery on the esophagus is necessary for such pathologies as diverticulosis (deformation of the wall of the esophagus with the formation of cavities in its wall, leading to the accumulation of food debris in them), the formation of malignant and benign tumors, chemical or thermal burns. It can be performed by a surgeon specializing in the treatment of thorax organs, a professional in the field of thoracic surgery.
What does he do?
The competence of a surgeon dealing with diseases of the thorax includes making a diagnosis using modern diagnostic methods (ultrasound, MRI, tomography, x-ray examination), deciding on the need for surgical intervention, performing an operation, and managing the patient in postoperative period. Thoracic surgery requires high qualifications, which is why most famous medical institutes have departments that train these specialists.
Methods for diagnosing chest diseases
Thoracic surgeons have access to a variety of cutting-edge or traditional diagnostic methods, which increases the accuracy of diagnosis and determines the effectiveness of subsequent treatment. Diagnostics are used using the following tools and methods:
- ultrasound examination;
- X-ray;
- CT scan of the chest;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- computed tomography;
- bronchoscopy;
- spirography;
- thoracoscopy;
- pleural puncture;
- biopsy;
- angiography (to determine the condition of blood vessels).
When is a consultation with a thoracic surgeon necessary?
Other specialists - therapists, pulmonologists, gastroenterologists, oncologists - often refer you for consultation to a surgeon involved in the surgical treatment of thorax organs. Self-referral to this highly specialized specialist is possible if you have symptoms such as difficulty breathing, impaired swallowing, persistent cough with purulent expectoration, traces of blood in the vomit, chest pain of a focal or general nature. Whether or not to admit you to a hospital for a comprehensive examination will be decided by the doctor conducting the initial consultation.