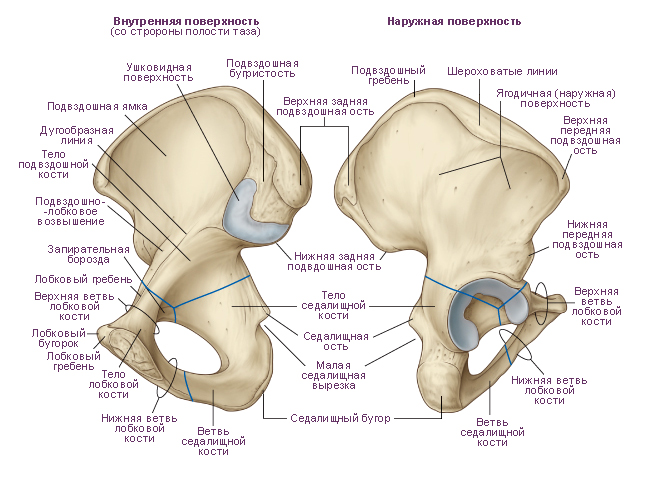
Ilium, os ilium, the largest of the bones that form the pelvic bone. The lower part of the bone is thickened and is called the body of the ilium, corpus ossis ilii. The body of the bone forms the upper part of the acetabulum. On the inner surface of the body there is an arcuate line, linea arcuata, above which is a wide, flattened part of the bone, called the iliac wing, ala ossis ilii. The lower section of the wing adjacent to the body is narrowed, the upper section is wide. Its edge is somewhat thickened and serves as a place of attachment of muscles, the trace of which remains on the bone in the form of three rough lines, or lips: the outer lip. liabium externum. inner lip, labium internum, and the intermediate line between them, linea intermedia.
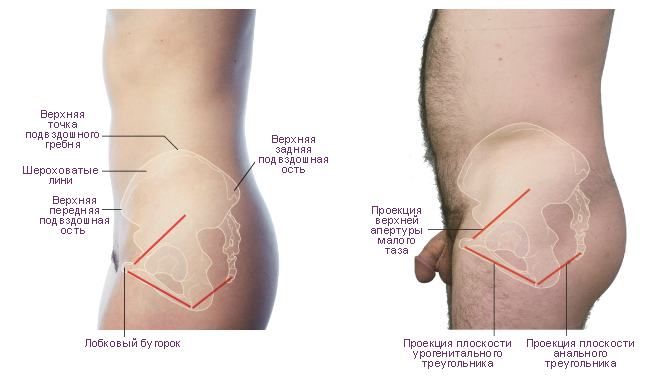
In general, the upper peripheral edge of the wing is called iliac crest. Crista Iliaca. It is S-shaped and ends in front with a well-palpable protrusion through the skin, which is called the superior anterior iliac spine, spina iliaca anterior superior, in the back - the superior posterior iliac spine, spina iliaca posterior superior. The anterior edge of the wing below the spina iliaca anterior superior has an iliac, or semi-lunar, notch, which is bounded below by the inferior anterior iliac spine, spina iliaca anterior inferior. Below it, the edge of the bone wraps anteriorly and reaches the iliopubic eminence, eminentia iliopubica, which is the site of fusion of the body of the ilium with the pubic bone.
The posterior edge of the wing below the spina iliaca posterior superior bears the inferior posterior iliac spine, spina iliaca posterior inferior, where the greater sciatic notch, incisura ischiadica major, begins, in the formation of which the body of the ischium is involved. The outer surface of the iliac wing - the gluteal surface, facies glutea, bears a trace of the gluteal muscles starting here - three gluteal lines: posterior, anterior and lower. The posterior gluteal line, tinea glutea posterior, is located in front of the spina iliaca posterior superior and runs from the outer lip of the iliac crest to the base of the inferior posterior iliac spine.
The anterior gluteal line, linea glutea anterior, starts from the superior anterior iliac spine and, heading backward, curves downward in an arcuate manner, reaching the upper edge of the large sciatic notch. The lower gluteal line, linea glutea inferior, is located above the upper edge of the acetabulum. The inner surface of the iliac wing in the anterior sections is smooth, slightly deepened and is called the iliac fossa, fossa iliaca. Its lower edge is bounded by an arcuate line.
In the posterior part of the inner surface of the wing, above the large sciatic notch, there is an articular ear-shaped surface, facies auricularis. In front and below, it is limited by the periarticular groove. Behind and above the ear-shaped surface is the iliac tuberosity, tuberositas iliaca.
Fracture of the ilium
Fractures of the ilium can be different, and they all require a different approach to treatment. Sometimes a doctor, in order to restore the ability of his patient to work, has to resort to surgical intervention. Sometimes conservative treatment is enough. Here we will analyze the most common types of iliac fractures.
Fracture of the iliac wing.
The cause of such a fracture is a blow or compression of the pelvis. In children, this injury can cause a sharp contraction of the gluteal muscles. The fragment can be quite large, sometimes it reaches half of the ilium.
Symptoms. The fracture site is swollen. Pain is noted, which increases when bending the leg in hip joint as well as any other movement of the legs. Often accompanied by hemorrhage, which extends not only to the lateral surface of the pelvis, but also to the upper third of the thigh. Trying to stand up causes a sharp pain. The function of the lower limb on the side of the lesion is sharply reduced. On palpation, the pain intensifies, sometimes you can hear crepitus (crunch) of fragments. Perhaps the tension of the muscles of the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall on the side of the lesion.
Treatment. The patient must be taken to the hospital in the supine position. There should be a cushion under the knees. First of all, the doctor does anesthesia to a patient with a fracture of the iliac wing. Often this is intrapelvic anesthesia - a solution of novocaine, or another local anesthetic, is injected with a long needle. Then bed rest is prescribed. The patient lies on his back, the leg is placed on the tire. This is necessary to relax the muscles. The duration of bed rest is 3-4 weeks. After its cancellation, physiotherapy exercises and physiotherapy are prescribed. As a rule, full recovery of working capacity occurs in a month and a half.
Avulsion of the anterior superior iliac spine.
Symptoms. Pain and swelling in the area of the fracture. Sometimes the muscles, contracting, pull the fragment towards themselves, causing it to move downward. In this case, the patient experiences a sharp pain while trying to take a step forward. The step back is much easier for him, it is less painful. The patient cannot walk normally, but can move backwards.
Treatment. The patient is laid on his back, the legs are fixed in a half-bent state. In this position, the patient is taken to the hospital. Next, the doctor conducts local anesthesia with novocaine. Sometimes, if there is too much displacement of the fragment, surgery may be necessary. The duration of bed rest is about two weeks. The patient lies on his back, the leg is placed in the tire. After three weeks, he is allowed to walk with a crutch or stick. Next, you need to gradually increase the intensity physical activity. After about a month and a half, the function of the limb is fully restored. After three months, the athlete can begin full-fledged training.
Fracture of the lower anterior iliac spine.
The quadriceps femoris muscle is attached to the lower anterior iliac spine. With its sharp reduction, a fracture of the bone protrusion occurs. The symptoms and treatment are the same as for the detachment of the anterior superior spine.
Vertical fracture of the iliac bone.
This is a very severe injury that leads to a violation of the integrity of the pelvic ring. At the same time, one part of the pelvis rises up, creating the illusion of a shortened limb. Often there is an extensive hematoma (hemorrhage), sometimes the pelvic organs are injured.
Treatment. First, local anesthesia with novocaine is done, then bed rest is prescribed. With these fractures, doctors often have to resort to surgical interventions. Skeletal traction for the lower limbs is also used. The consequences of a pelvic fracture have many nuances. Rehabilitation of patients is long. Walking is allowed only after three months. It takes about five months to fully recover.
Displaced coccyx fracture
The coccyx is the lowest (rudimentary or caudal) section of the spine, which consists of 4-5 poorly developed vertebrae. In the process of evolutionary development of mammals, the coccyx acquired the status of a rudimentary organ, however, it did not lose its functional significance. This is the place of attachment of the system of muscles and ligaments of the pelvic organs.
Fractured hand in a child
Children lead a more active lifestyle and therefore injuries in childhood widespread enough. It should be noted that this type of injury, such as a broken arm, can occur with a mild household, sports or street injury when falling from a height, while exercising in the sports section, running, walking, playing on the playground or in the house.
Fractured little finger
Doctor A. Deryushev
A fracture of the little finger on the hand usually occurs due to direct trauma. This situation can be caused by injury from a blow, a fall, and also under the influence of a heavy object. Like any other bone fracture - fractures of the little finger or fifth finger of the hand can be open, that is, accompanied by damage to the skin and closed - when such damage is not determined.
The consequences of a fracture of the cervical vertebra
Fractures of the cervical spine often occur not only as a result of strong extension or flexion of the neck, but sometimes after a rather awkward turn of the head in some direction, and even after a birth injury.
It is formed by the bone base (pelvic bones), muscles (pelvic muscles) and filled with internal organs (organs of the pelvic cavity).
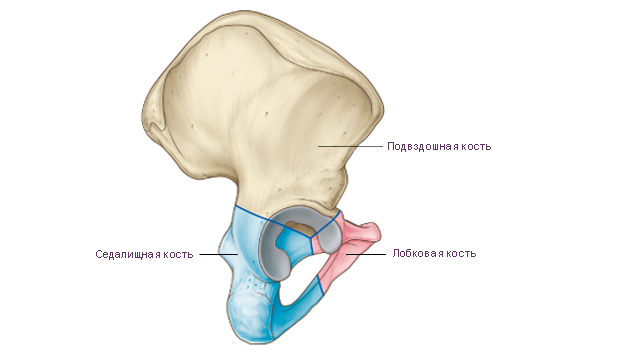
Hip bone An adult human is made up of three fused bones: the ilium, pubic bone, and ischium. Before the age of 12-16, these individual bones are connected by cartilage. The place of fusion of the bodies of these bones is deep acetabulum. It is the articular fossa for the head of the femur. The acetabulum has a high edge around the circumference. On its medial side is notch of the acetabulum. For articulation with the head of the femur in the acetabulum, along its periphery, there is a lunate surface. In the center of the acetabulum is fossa of the acetabulum.
Ilium consists of two departments. The lower thickened section is called body of the ilium. The body is involved in the formation of the acetabulum. The upper extended section is called iliac wing. The wing is a wide curved plate, thinned in the center. At the periphery, the wing is thickened, widens fan-shaped and ends iliac crest. The iliac crest shows three rough lines for attachment of the broad abdominal muscles. These formations are called: outer lip, inner lip and intermediate line. The iliac crest has bony prominences anteriorly and posteriorly. The protrusions located in front are called superior anterior iliac spine And inferior anterior iliac spine. The protrusions located at the back are called superior posterior iliac spine And inferior posterior iliac spine.
On the outer surface of the iliac wing, three faint rough lines can be seen, on which the gluteal muscles begin and the fascia covering them. Anterior gluteal line the longest. It begins near the superior anterior iliac spine, goes in an arcuate direction towards the greater ischial notch of the ischium. Posterior gluteal line located almost vertically and parallel to the posterior section of the previous line. Lower gluteal line shorter than others. It starts between the superior and inferior anterior iliac spines and runs over the acetabulum to the greater ischial notch.
On the inner surface of the iliac wing there is a gentle depression. He is called iliac fossa. The inferior border of the iliac fossa is arcuate line. The arcuate line reaches behind the anterior margin ear-shaped surface. This surface serves to articulate with the corresponding surface of the sacrum. The arcuate line continues anteriorly into the iliopubic eminence. Above the ear-shaped surface is iliac tuberosity for attachment of interosseous ligaments.
Pubic bone has an extended part - the body, and two branches. Body of the pubic bone forms the anterior part of the acetabulum. Goes anteriorly from the body superior branch of the pubis from iliopubic eminence located along the line of fusion of the pubic bone with ilium. The anterior part of the upper branch bends sharply downwards and passes into inferior pubic ramus. In the region of the medial edge of the pubic bone is an oval symphysial surface. It serves to connect with the paired pubic bone of the opposite side. On the upper branch of the pubic bone, near its medial end, there is pubic tubercle. On the posterior surface of the lower branch of the pubic bone in the direction from back to front and medially passes obturator groove. The blood vessels and the nerve of the same name pass through it.
Ischium has a thickened body. Body of ischium complements the bottom of the acetabulum and anteriorly passes into branch of ischium. The body of the ischium with its branch forms an angle open anteriorly. In the region of this angle, the ischium has a thickening - ischial tuberosity. Above the ischial tuberosity, from the posterior edge of the body of the ischium, ischial spine. The ischial spine separates two notches: the lower small ischial notch and top greater ischial notch. The branch of the ischium is connected to the lower branch of the pubic bone. This connection closes the bottom of the oval obturator foramen.
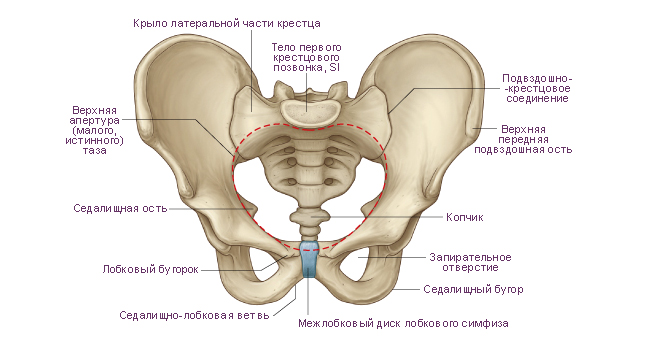
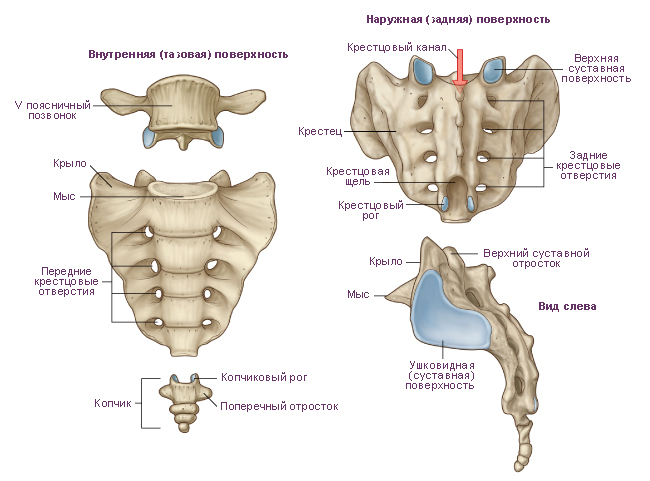
Sacrum consists of five sacral vertebrae. These vertebrae fuse into one bone during adolescence. The sacrum has a triangular shape. It is a massive bone and takes on the weight of almost the entire body. There are the following structures of the sacrum: base of the sacrum, the top of the sacrum, pelvic (inner) surface of the sacrum And dorsal (outer) surface of the sacrum. The base of the sacrum is connected with the lower articular processes of the 5th lumbar vertebra with the help of articular processes. In the area of the connection of the base with the V lumbar vertebra, a rounded corner protrudes forward - cape sacrum. On the concave pelvic surface, facing forward, four transverse lines. These are traces of fusion of the bodies of the sacral vertebrae with each other. On each side at the level of these lines there are pelvic sacral openings. On the convex dorsal surface of the sacrum are visible on each side dorsal sacral foramen. As a result of fusion of the processes of the sacral vertebrae, five longitudinal ridges were formed. Unpaired median sacral crest are the fused spinous processes of the sacral vertebrae. Doubles intermediate comb is the result of fusion of the articular processes of the sacral vertebrae, and the paired lateral sacral crest formed by fusion of the transverse processes of the sacral vertebrae.
On the upper lateral parts of the sacrum are ear-shaped surfaces for articulation with the same-named surfaces of the iliac bones. On each side between the ear-shaped surface and the lateral crest there is sacral tuberosity to which ligaments and muscles are attached. The vertebral foramina of the fused sacral vertebrae form sacral canal. This channel opens below sacral fissure. The gap is limited on the sides sacral horns, which are vestiges of the articular processes.
Coccyx consists of 3-5 rudimentary coccygeal vertebrae. The coccygeal vertebrae are connected in childhood with layers of cartilage. These vertebrae fuse into one bone during adolescence. The coccyx has the shape of an anteriorly curved triangle. The base of the coccyx is turned up, the tip is directed down and forward. For articulation with the sacrum there are coccygeal horns corresponding to the sacral horns. At a young age, especially in women, the coccygeal vertebrae are connected using layers cartilage tissue.
|
Scheme. Upper pelvic aperture. |
|
 |
|
|
Scheme. Features of the position of the pelvis in the body of a man and a woman. Left side view. |
|
 |
|
|
Scheme. Hip bone. |
|
 |
|
|
Scheme. sacrum and coccyx. |
|
 |
|
|
Scheme. Right pelvic bone. |
|
|
|
|
Premise: |
Ilium, os ilii (ilium) (see Fig.,,,,), - the largest of the bones that form the pelvic bone. The lower part of the bone is thickened and is called the body. Body of the ilium, corpus ossis ilii, represents the upper division acetabulum, acetabulum, posterior and upward from which is located supraacetabular groove, sulcus supraacetabularis(place of attachment m. retus fempris). On the inner surface of the body arched line, linea arcuata, above which is a wide, flattened part of the bone, called iliac wing, ala ossis ilii.
The lower part of the wing adjacent to the body is narrowed, the upper part is wide. The edge of the wing of the ilium is somewhat thickened and serves as a place of attachment of muscles, from which three rough lines remain on the bone: outer lip, labium externum, inner lip, labium internum, And intermediate line. On the outer lip there is a small iliac tubercle, tuberculum iliacum, located 5-7 cm posterior to the superior anterior iliac spine. In general, the upper peripheral edge of the wing is called iliac crest, crista iliaca. It is S-shaped and ends in front with a well-palpable protrusion through the skin - superior anterior iliac spine, spina iliaca anterior superior, behind - superior posterior iliac spine, spina iliaca posterior superior.
The anterior edge of the wing below the superior anterior iliac spine has a crescent-shaped notch, which is limited below lower anterior iliac spine, spina iliaca anterior inferior. Below it, the edge of the bone wraps anteriorly and reaches iliopubic eminence, eminentia iliopubica, which is the site of fusion of the body of the ilium with the pubic bone. The posterior edge of the wing below the superior iliac spine has lower posterior iliac spine, spina iliaca posterior inferior, - starts here greater ischial notch, incisura ischiadica major, in the formation of which the body of the ischium participates.
Outer surface of the iliac wing gluteal surface, facies glutea, is the site of the beginning of the gluteal muscles. It has three gluteal lines: back, front and bottom.
Posterior gluteal line, linea glutea posterior, located in front of the superior posterior iliac spine, goes from the outer lip of the iliac crest to the base of the inferior posterior iliac spine.
Anterior gluteal line, linea glutea anterior, starts from the superior anterior iliac spine and, heading back, curves downward in an arcuate manner, reaching the upper edge of the large sciatic notch.
Lower gluteal line, linea glutea inferior, is located above the upper edge of the acetabulum.
The inner surface of the iliac wing in the anterior sections is smooth, slightly deepened and is called iliac fossa, fossa iliaca. Its lower edge is bounded by an arcuate line. The posterior part of this surface, facing the sacrum, is uneven and is called sacro-pelvic surface, facies sacropelvina(see fig.).
IN sacral region sacroiliac surface, above the greater sciatic notch, is the articular auricular surface, facies auricularis, bounded in front and below by a furrow. Posterior and superior to the ear-shaped surface is located iliac tuberosity, tuberositas iliaca.
It is one of the parts of the back wall of the abdomen and has the shape of a cavity. Its upper border is the ilium (PC), in particular its crest, the anterior border is the beginning of the bone and ligament, the internal one is the connection with the sacrum, the lower border is the nameless line. In this case, the PC acts as the skeleton of this area, to which the muscles of the posterior wall of the abdomen are attached. Together, muscles and bones form a tight sheath.
Thus, large iliac bones are attached to the sacrum on both sides, which have rounded tops, therefore they are well palpable on the human body.
The ilium is the largest of all the bones that form the pelvic region of the human skeleton. Its lower part is somewhat thickened and is called the PC body, which forms the upper part of the acetabulum. The sacrum and femur are connected to the body of the ilium. During puberty, the PC fuses with the pubic bone and in the area thus forming the pelvic bone.
On the inner side of the body there is a line in the form of an arc, and above is a wide part of the bone, called the wing of the PC, the lower part of which is narrowed, and the upper one is expanded. The edge of the wing is thickened, the abdominal muscles are attached to it, traces of which are imprinted on the bones in three lines (lips): outer, inner and intermediate. It should be noted that the upper parts of the wings are called the iliac crests. The crest has an S-shape and ends in front of the anterior superior PC, which can be felt on the human body through the skin, and in the back - with the posterior superior iliac bone.
Note that the anterior edge of the ilium fuses with and the posterior edge borders on the ischial notch. The outer part of the wing is the place of attachment of the gluteal muscles, and on the inner part of the wing, called the iliac fossa, there is an articular ear-shaped surface, which is the junction with the surface of the sacrum. Above it is the iliac tuberosity, which serves to attach the ligaments.
The iliac fossa is the site of attachment of the iliac muscle. It is adjacent to the muscle lumbar and originates from the upper part of the fossa, the inner lip of the crest and the anterior sacral and lumbar ligaments. Together with the psoas major muscle, the iliac muscle is involved in the formation of the muscle mass of the wall. abdominal cavity(rear). Also, its functions include hip flexion.
So, top part The PC is rounded, the front and back form two ledges each, and the outer part is somewhat elevated. In general, the relief of the bone depends on the muscles, in the places of attachment of which various lines, ridges, pits and spines have formed.
Thus, the ilium is one of the three components that form a single pelvic bone. In humans, it connects to the sacral bone (fusion of five vertebrae) and fuses with the other two components of the pelvis in the region of the acetabulum. Muscles are attached in this area, in particular the iliopsoas, which, due to its contractions, makes the limb move forward, that is, controls their movement, and also stabilizes the pelvis, flexes the hip and lumbar spine.
Summing up, it should be noted once again that the ilium, the function of which is to strengthen the muscles, participates in the process of formation and control of movements. lower extremities. Connected to the joints and driven by the muscles, the PC also forms a protection for the soft parts of the body, while simultaneously ensuring its smoothness of movement. In addition, being part of the human skeleton, the ilium serves as a frame to which others, namely the lower limbs, are attached.