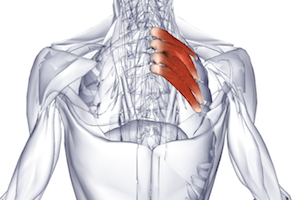
There are a lot of different muscles in the human body. In particular, there are those on the back that allow the ribs to rise and fall.
With certain diseases of the spine, characteristic pain is felt at the location of the serratus back muscles. To eliminate the symptoms of the pathology, special treatment is provided.
General characteristics
In the spine area, parallel to the ribs, there are two thin and flat muscles - the serratus dorsi. They are the connecting link between the intercostal muscles and the pectoral muscles.
With the correct development of the serrated organs, consisting of muscle tissue, any of their bundles will be clearly visible.
Muscles should be distinguished:
- upper posterior dentate,
- lower serrated
The place where the rear upper serratus muscle back, – area under . It originates from where the spinous processes of the vertebrae are present - I-II thoracic and VI-VII cervical.
Attachment to the back of the II-V ribs is carried out using four teeth (branches), while the serratus superioris muscle is located in the direction from top to bottom along an oblique line.
The second type begins at the location of the spinous processes of the vertebrae - XI-XII thoracic and I-II lumbar. At the very beginning, the lower posterior serratus dorsi muscle looks like a tendon plate, like the previous organ.
The posterior muscle is attached by separate branches to the IX-XII ribs.
Both the first and second organs accept active participation in the respiratory process. The task of the upper muscle is to raise the ribs, the lower, in turn, lowers them.
With the simultaneous action of these organs, expansion occurs chest.
Upper muscle lesion
When osteochondrosis of the upper thoracic vertebrae occurs, doctors diagnose serratus superioris syndrome. The pathology may be accompanied by dull and deep pain in the area:
- upper edge of the scapula,
- shoulder,
- triceps muscle.
Such signs can be taken as a manifestation of compression of the nerve roots. True, no neurological disorders are detected.
On palpation, thickening and painful discomfort are felt. The patient may feel pain in the chest.
An external examination will show that there is no roundness of the shoulders, as happens when the rhomboid and pectoralis major muscles are affected. The shoulders and shoulder girdle area are not limited in movement.
Physical activity has practically no effect on the intensity of manifestations. However, if you lift weights in such a way that the shoulder blade presses on the affected area, the pain will intensify.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor uses the palpation method. The patient, sitting on a chair, should bend slightly. The arm that is on the side where the examination is being carried out should hang freely.
Or you can place the hand in the muscle cavity on the opposite side to fully abduct the shoulder blade.
Elimination of the syndrome is carried out using:
- post-isometric relaxation,
- ischemic compression.
When using the second method, the patient is allowed to both sit and lie, turning onto his stomach.
Lower muscle damage
The serratus inferior dorsi muscle may lose its function when the upper and lower thoracic vertebral segments are affected. Location of pain:
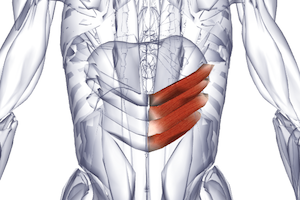
- lower back,
- area of the lower ribs.
This symptom is characterized by aching, chronic nature. Due to severe tension, movements of the thoracolumbar region are limited.
If such signs appear, the spinal column and chest organs must be examined to exclude the development of pleurisy.
Palpation helps identify tender, painful areas in the area where the muscles connect to the ribs.
To treat the syndrome, the same methods are prescribed as in the previous case.
When performing post-isometric relaxation, the patient can sit or lie on his side. If the patient is sitting, do the following:
- By moving the shoulder forward, the doctor first stretches the muscle. At the same time, the patient’s torso is slightly bent so that there is a slight and comfortable feeling of tissue tension. Getting used to stretching lasts approximately 3-5 seconds.
- The patient should inhale smoothly and slowly, and then, stopping breathing, try to assume a neutral position. In this case, there is slight resistance on the part of the specialist. The effort required is minimal.
- A slow exhalation is made, the back relaxes, and the doctor performs a passive stretch with an increase in the initial displacement of the body.
- The procedure should be carried out without stopping 4-6 times.
To perform ischemic compression, the patient must lie on his stomach or side. In the first case, the specialist will perform sliding thumbs hands on the muscle.
If a very painful point is identified, then a slow deep massage is performed in this place.
As medical practice shows, the effectiveness of treatment increases when ischemic compression is performed before the stretching procedure.
All back muscles have their own purpose. And if problems arise with them, unpleasant manifestations will not take long to appear. To ensure your back always remains healthy, you need to consult a specialist in time.
Advanced pathologies require long-term treatment and often result in complications. Therefore, you should pay attention to the slightest discomfort in the back and follow all medical instructions.
By the way, now you can get my free e-books and courses that will help you improve your health and well-being.
In addition, if you want to restore the health of your spine and joints, and also maintain it for a long time, then I have special step-by-step exercise programs that I recommend that you do regularly.
In addition, you can also order my first printed book entitled "A Healthy Spine in 2 Weeks: 86 Essential Exercises" from online bookstores.
Disclaimer
The information in the articles is for general information purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. This article is not a substitute for medical advice from a doctor (neurologist, therapist). Please consult your doctor first to know the exact cause of your health problem.
I will be very grateful if you click on one of the buttons
and share this material with your friends :)
Raises II, III, IV, V ribs (Fig. 13a).
Start: from the spinous processes of the last two cervical vertebrae and the first two thoracic vertebrae
Attachment: II - V rib
Innervation: nn. intercostales Thl-Th4
Diagnostics: The patient sits slightly leaning forward, the arm on the side being examined hangs freely; You can place her hand in the opposite armpit for more complete abduction of the scapula. The scapula should be displaced laterally and retracted to expose the TZ located in the muscle. The serratus posterior superior muscle is palpated through the trapezius and.
Rice. 13a. Serratus posterior superior muscle - m. serratus posterior superior
Vigorous palpation produces a local twitch response in the trapezius muscle fibers, which are recognized by their horizontal orientation. TZ localized in the posterior superior serratus muscle is revealed as an area of extremely deep pain in the muscle band when it is pressed against the underlying rib. Pressure on these TZs clearly produces a characteristic pattern of referred pain.
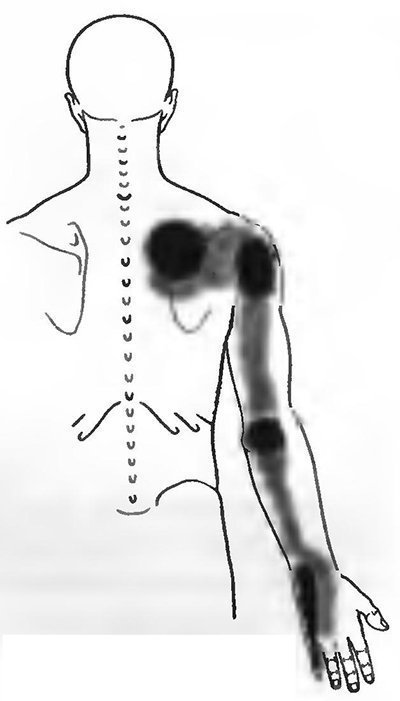
Rice. 13b. Referred pain
(Fig. 13b): TK of this muscle often causes pain in the scapula and shoulder area. Characteristic of damage to the posterior superior serratus muscle is a dull, deep pain under the upper edge of the scapula. The pain is localized even deeper than the pain pattern caused by TZ in the middle portion of the trapezius muscle. Along with this, quite intense pain is felt over the posterior edge of the deltoid and long head of the triceps brachii muscle.
It often affects the entire area of the triceps muscle with its epicenter in the area of the internal epicondyle of the shoulder, and sometimes spreads along the ulnar surface of the forearm and metacarpus, including the entire little finger. Anteriorly, the pain may spread to the chest.
Shifts the lower ribs posteriorly and downward and thereby promotes expansion of the chest in the lower part (deep breath).
Start: from the spinous processes of the XII thoracic vertebra and the first three lumbar vertebrae (Fig. 14a)
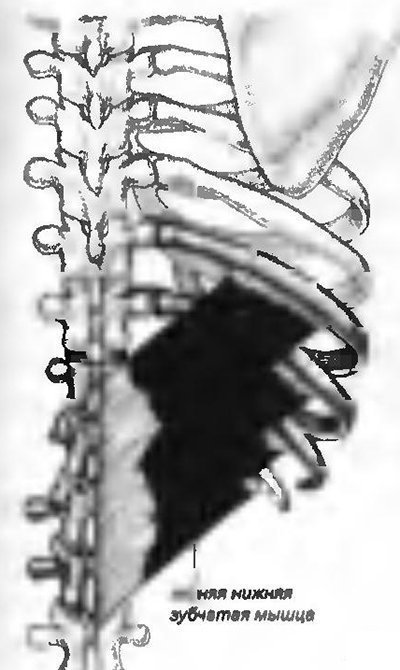
Rice. 14a. Serratus posterior inferior muscle - m. serratus posterior inferior
Attachment: IX - XII rib.
Innervation: nn. intercostales T9-T12
Diagnostics: Painful TZs are detected by superficial palpation at the sites of muscle attachment to the ribs.
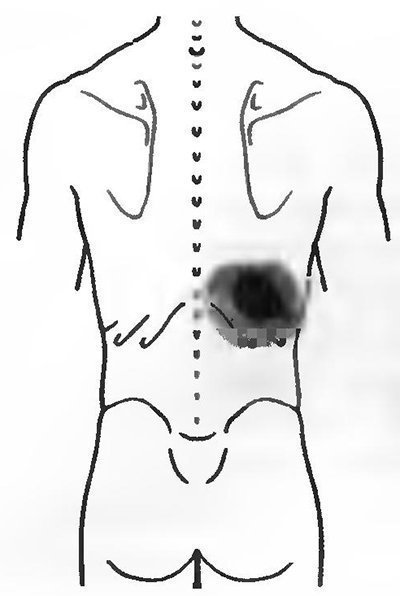
Rice. 14b. Referred pain
(Fig. 14b): Active TZ in the serratus inferior posterior muscle causes pain in the lower back and lower ribs.
R.G. Esin, O.R. Esin, G.D. Akhmadeeva, G.V. Salikhova
The serratus posterior superior muscle is located on the human back and is one of the superficial muscles. It is paired, attached directly to the rib and, in comparison with other superficial ones, lies deep.
General information
The named muscle is located under the rhomboid. It belongs to the third layer of muscles covering the human back. In structure, this organ is flat. Nuchal ligament - its lower part is the place where the serratus muscle is attached. The bundles of the latter are directed downward, obliquely, passing to the outer surface of 2-5 ribs, to which they are attached, lateral to their corners.
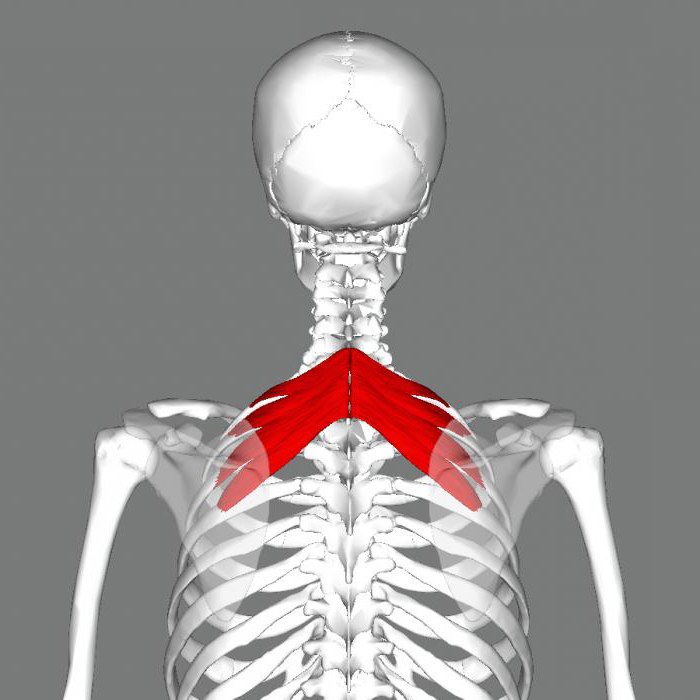
The muscle, the beginning of which is the nuchal ligament, depending on the fitness of the body, may have large number bunches, or maybe completely absent.
When it contracts, the upper part of the ribs that make up the chest rises, which allows a person to breathe.
nearest neighbor
The superior serratus posterior muscle is located in close proximity to the inferior muscle of the same name. And that one is next to the widest spinal muscle, directly in front of her. The muscle also originates from the tendon plate, but located on the 1st and 2nd lumbar, as well as on the 11th and 12th thoracic vertebrae.
This muscle is also oblique, it is directed upward and laterally. The muscle is involved in the act of inhalation and exhalation, as it lowers the ribs of the chest in its lower half.
Operation
Both muscles described are classified as the main respiratory muscles, since their contractions provide the ability to inhale.
In order for the serratus posterior superior muscle to function correctly, blood flow to it is carried out by an artery located between the ribs. Another source of necessary nutrients- deep cervical artery. Intercostal nerves provide innervation to the organ.
Why does the muscle hurt?
The serratus posterior superior muscle tends to be of concern in cases of osteochondrosis affecting the intervertebral discs in the upper part of the chest. The first symptom of the disease is dull severe pain in the depths, near the shoulder blade.
To diagnose the problem, palpation is carried out by slightly moving the scapula followed by placing the hand in armpit on the opposite side of the body. In this case, the patient’s torso should be slightly tilted forward, allowing the arms to hang freely.
Myofascial syndrome
MFPS is diagnosed by dull, constant, severe pain, which is local and segmental in nature. In this case, so-called trigger points are observed where the pain is concentrated. When palpating along the muscle, nodules can be detected. The neoplasms are located strictly along the muscle fibers and grow 2-5 mm in diameter.
Palpation is accompanied by severe local, referred pain. Each has its own pain zone and paresthesia. Upon contact with the area, “jumping syndrome” occurs, when the patient reflexively tries to move away from the source of sensations. This sign is considered a typical manifestation of MFPS.
In addition to active trigger points, there are latent ones. The first are characterized by spontaneous sharp sensations that accompany muscle loading and palpation. For the latter, spontaneity of the pain syndrome is not typical.
If the described points are present in a latent form, the upper posterior dentate organ weakens, is depressed, and fatigue increases. If there are 2-3 points in an organ, between which there is a nerve or a bundle of them, there is a high probability of developing neurovascular compression.
MFPS is formed when a muscle is stretched or undergoes sudden movements. There is a high probability of MFPS if the patient spent a long time in an uncomfortable antiphysiological position, was exposed to abnormally low or high temperature. The syndrome is observed with different leg lengths, anomalies in the development of the pelvic ring and foot. In some cases the reasons will be:
- mental disorders;
- metabolic disorders;
- poor nutrition.
Trigger points are activated when:
- pneumonia;
- emphysema;
- asthma.
The pain associated with MFPS is reflected in the lower ribs, in the sternum from below. The syndrome can be triggered by work that forces a person to spend a long time standing with his arms raised.
Workout
The serratus posterior superior muscle is pumped up during comprehensive back muscle training. The most useful exercise is called “pullover”. In addition to this, they practice:
- deadlift;
- bent over row;
- traction horizontally;
- shrugs (using dumbbells, barbells);
- tilts, weighted with a barbell;
- T-bar row.
- Exercise regularly 2-3 times a week. The first results will be noticeable in just 3 weeks.
- Warm up before starting class. If you experience pain, you need to reduce the load or even stop the practice completely until the body recovers. Remember: excess weight displaces the vertebrae, causing hernias and injuries.
- Carefully control your breathing.
- Follow the technique of each exercise, keeping your back straight.
- Increase the load gradually.
- Eat right.
- Control your sleep and wakefulness patterns.
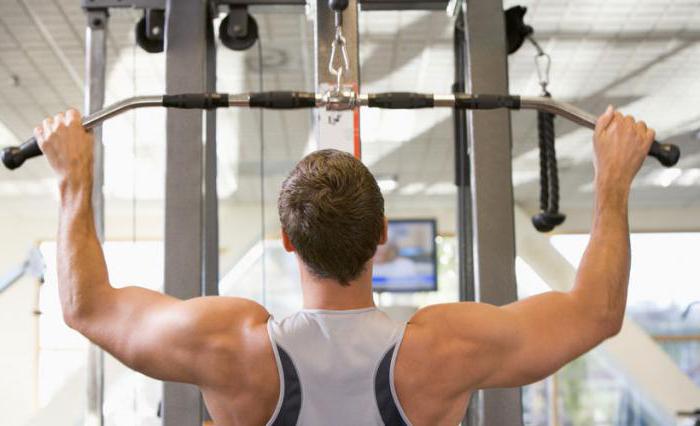

Don't try to do all the exercises in one workout. Alternate them according to a pre-designed program so that the load is different days was on different areas of the back. An integrated approach will help you become stronger, train your muscles, achieve beautiful figure. Don't try to focus solely on the serratus posterior superior muscle; instead, engage your entire back in the program.
text_fields
text_fields
arrow_upward
On the back, as in the chest area, the intrinsic muscles lie deep and are covered with alien muscles that move the upper limbs and strengthen them on the body.
The intrinsic muscles of the back of ventral origin include two underdeveloped muscles ending on the ribs: the posterior superior and posterior inferior serratus.
- Serratus posterior superior muscle(i.e. serratus posterior superior) starts from the spinous processes of the two lower cervical and two upper thoracic vertebrae.
- Serratus posterior inferior muscle(t. serratus posterior inferior) starts from the lumbar-dorsal fascia at the level of the two lower thoracic and two upper lumbar vertebrae. Both muscles are involved in the respiratory act: the upper one – raising, and the lower one – lowering the ribs. Acting simultaneously, they expand the chest.
Beneath both serratus posterior muscles along the spinal column lie the deep back muscles. These are the own muscles of the trunk, having a dorsal origin. In humans they retain a primitive, more or less metameric arrangement.
The deep back muscles lie on either side of the spinous processes of the spine, extending from the sacrum to the skull. They can be distinguished four muscle tracts, sequentially located in the direction inward.
Splenius muscle of the head and neck
text_fields
text_fields
arrow_upward
I tract(only on the neck) is represented by the splenius muscle of the head and neck (i.e. splenius capitis et cervicis), which starts from the spinous processes of the upper thoracic and lower cervical vertebrae and is attached to the transverse processes of the I and II cervical vertebrae and to the mastoid process temporal bone. With a bilateral contraction, the muscle bends the head and neck back; with a unilateral contraction, it turns them.
Erector spinae muscle
text_fields
text_fields
arrow_upward
II tract formed by the erector spinae, which starts from the posterior surface of the bone and the thoracolumbar fascia. The muscle extends the spine and plays a large role in its statics.
Below the XII rib, the erector spinae is divided into three muscles: the iliocostal, longissimus and spinalis muscles.
Iliocostal muscle
text_fields
text_fields
arrow_upward
The iliocostalis muscle is the most lateral muscle, attached to the ribs and transverse processes of the lower cervical vertebrae.
Longissimus dorsi muscle
text_fields
text_fields
arrow_upward
Longissimus muscle the back is attached to the transverse processes of all the thoracic and cervical vertebrae and ends on the mastoid process of the temporal bone.
Spinalis dorsi
text_fields
text_fields
arrow_upward
The spinalis dorsi muscle is attached to the spinous processes of the thoracic and cervical vertebrae up to the epistrophy.
- III tract consists of the transverse spinalis muscle (i.e. transversospinalis), which stretches from the sacrum to the occipital bone, and its bundles are directed from the transverse processes to the spinous ones. The muscles of this tract extend the spine, tilt it to the sides, and also rotate it.
- IV tract form the short intertransverse and interspinous muscles of the back in the cervical and lumbar regions, and the short occipitovertebral muscles.
Intertransverse muscles
text_fields
text_fields
arrow_upward
The intertransverse muscles are located between the transverse processes of adjacent vertebrae: when contracted, they participate in abducting the spine to the sides.
Interspinous muscles
text_fields
text_fields
arrow_upward
The interspinous muscles are located between the spinous processes of adjacent vertebrae; during contraction, they participate in the extension of the spine.
Short occipitovertebral muscles
text_fields
text_fields
arrow_upward
The four short occipitovertebral muscles are located between the occipital bone, the atlas and the epistropheus. The muscles extend and rotate the head.
The diversity of the deep muscles of the back is associated with a great differentiation of movements of the spine and the whole body. The power of this muscle ensures a person’s vertical position. Without the deep back muscles, a person's torso would bend forward because its center of gravity lies in front of the spine.
The group of alien muscles on the back associated with the upper limbs is located in two layers. In the superficial layer lie the trapezius muscle that came from the head (branchial origin) and that came from upper limb latissimus dorsi muscle.
Trapezius muscle
text_fields
text_fields
arrow_upward
The trapezius muscle (t. trapezius) originates from the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone, the nuchal ligament and the spinous processes of all thoracic vertebrae. The muscle fibers converge outward and attach to the outer end of the clavicle, to the spine and acromial process of the scapula. The lower muscle bundles, contracting, lower the shoulder girdle, the middle ones pull it towards the spine, the upper ones lift it; the superior bundles work as synergists of the serratus posterior muscle when it abducts the arm above the level shoulder joint. At fixed shoulder girdle The trapezius muscle pulls the head back.
Serratus posterior superior, m. serratus posterior superior, is a thin muscle, covered by the rhomboid muscle and forms the third layer of the superficial muscles of the back.
It starts from the lower part of the nuchal ligament and the spinous processes of the two lower cervical and two upper thoracic vertebrae. Its bundles are directed obliquely downwards and laterally and are attached by four teeth to the outer surface of the II-V ribs, somewhat lateral to their corners.
Function: raises the upper ribs, participating in the act of inhalation.
Innervation:nn. intercostales (ThI-ThIV).
Blood supply: ah. intercostales, cervicalis profunda.
- - see t. 2, List of anat. terms...
Large medical dictionary
- - a muscle that begins with several teeth resembling saw teeth. For example, the serratus anterior muscle, a muscle that starts in large teeth from the upper eight to nine ribs and attaches to the scapula, is adjacent...
Medical terms
- - m. tibialis posterior, located between the two muscles described above, directly on the interosseous membrane...
Atlas of Human Anatomy
- - m. scalenus posterior, starts from the posterior tubercles of the V-VI cervical vertebrae, goes down behind the middle scalene muscle and attaches to the outer surface of the II rib...
Atlas of Human Anatomy
- - m. serratus posterior inferior, just like the previous one, is flat, thin, located under m. latissimus dorsi...
Atlas of Human Anatomy
- - m. serratus anterior, flat, wide, located in the anterolateral part of the chest wall. Upper part her covered big pectoral muscle, the lower one lies superficially, covered by the pectoral fascia...
Atlas of Human Anatomy
- - see List of anat. terms, 10...
Large medical dictionary
-
Large medical dictionary
- - see List of anat. terms...
Large medical dictionary
- - see List of anat. terms...
Large medical dictionary
- - see List of anat. terms...
Large medical dictionary
- - see List of anat. terms...
Large medical dictionary
- - see List of anat. terms...
Large medical dictionary
- - see List of anat. terms...
Large medical dictionary
- - see List of anat. terms...
Large medical dictionary
- - see List of anat. terms...
Large medical dictionary
"Serratus posterior superior muscle" in books
Back cover
From the book of Wanderings by Menuhin YehudiBack cover
Back cover
From the book Between the Closet and the Sky author Vedenyapin Dmitry YurievichBack cover The main pathos, as it seems to me, of both prose and lyrics of Dmitry Vedenyapin is gratitude. An enviable arrangement of soul and talent! Sergey Gandlevsky The poems of Dmitry Vedenyapin carve out a certain light cube in the world. in which any scene takes on character
Back cover
From Bulgakov's book without gloss author Fokin Pavel EvgenievichBack cover What kind of person was Bulgakov? This can be answered immediately. Fearless - always and in everything. Vulnerable, but strong. Trusting, but not forgiving of any deception, any betrayal. Embodied conscience. Incorruptible honor. Everything else in it, even very
Back cover
From Tsvetaeva's book without gloss author Fokin Pavel EvgenievichBack cover The same question is often asked: “What was she like?” Which! And, realizing the hopelessness of the answer, for some reason you still answer - difficult! Difficult and different, with different things, with the same things. But not from those different - different, with whom she is, but from herself
Back cover
From the book Dostoevsky without gloss author Fokin Pavel EvgenievichBack cover Dostoevsky's personality attracts attention as powerfully as his work. The life story of this person is beyond my comprehension. It seems sometimes that fate deliberately played with him all the known, conceivable and inconceivable variations of human life.
REAR CENTERING
From the book From Behind the Desk to War author Kravtsova Natalya FedorovnaREAR CENTERING Timokha and Victor were the first to reach the hangar. When the others approached, they had already pulled back the large bolt and opened the desperately creaking door. “Come in!” - Timokha invited and he himself entered before everyone else. The shed was very small. Through the cracks in the walls
3. PUBOCOCCOGYGEUS MUSCLE AND “QI MUSCLE”
From the book Improving Female Sexual Energy by Chia Mantak3. THE PUBOCOCcygeal MUSCLE AND THE “QI MUSCLE” Around the periphery of the vagina, at a depth of about one finger joint, you can feel the edge of the pubococcygeus muscle, sometimes called the “muscle of love” (Fig. 2-5). The contraction of the vagina is the compression pubococcygeus muscle. You surely
Details of ancient walls: location of towers, battlements, machicolations
From the author's bookDetails of ancient walls: location of towers, battlements, machicolations Therefore, Europe soon switched to stone fences, which were walls that usually surrounded the city and had towers at the corners or, if longer, in the middle (Fig. 2-a). The walls were made high (from 6 m and
Gear
From the book Great Encyclopedia of Technology author Team of authorsGear transmission A gear transmission is a mechanism designed to transmit rotational motion occurring between shafts, as well as to transform the rotational speed, which is based on the use of a gear connection.
Helical gear
From the book Great Soviet Encyclopedia (VI) authorToothed kinix, or Schweigger's turtle The toothed kinix lives in Africa in the territory from Uganda to the Atlantic coast. Other subspecies of this turtle are also known, distributed in the southern and eastern parts of Africa. The serrated quinix is a good swimmer, so