Consequences of a pelvic fracture
It should be noted that every third patient admitted to the department with a pelvic fracture is in traumatic shock, which is often caused by massive bleeding and injuries. internal organs.
The pelvis is the support of the spine and skeleton. It is located at the base of the spine and connects the limbs to the trunk. In addition, the pelvic bones and the bone bed (or pelvic ring) is a receptacle for the internal pelvic organs.
The authors point to the coincidence in such cases of bradycardia and hypotension, which distinguishes them from patients suffering from hemorrhagic shock. The matter seems to be simple, because the unconscious patient may be missed in the unconscious patient, and consciousness may be the dominant symptom to the extent that it "covers" all the others. A few years ago we had a patient initially hemodynamically stable with rapidly growing paresis. lower extremities. Computed tomography confirmed a vertebral fracture, while the patient's condition deteriorated rapidly; Behind a short time he was rushed to the operating room, where he died from a massive hemorrhage from an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
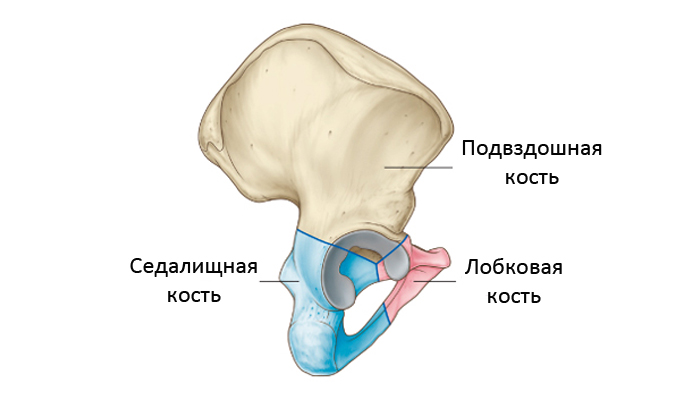
The pelvic ring is formed by the pubic, ilium, ischium and sacrum. The pelvic cavity houses the bladder, rectum, uterus, and vagina in women and the prostate and seminal vesicles in men. Most often, fractures of the ischial and pubic bones occur.
Causes of pelvic fractures complicated by damage to internal organs
This is why the percentage of so-called avoidable deaths has become one of the indicators of competence and competence in traumatic injuries. Pelvic fractures in case of multiple injuries. Pelvic fractures are associated with long-term failure as well as high mortality. In these cases, a well-documented complex algorithm has not yet been developed. After 8 weeks, the experiment was restarted, so both classification systems are useful for planning the treatment of patients with pelvic fractures.
Thus, the transverse compression, anteroposterior, and vertical shear fracture types are mainly explained by the choice of the correct surgical strategy for stabilizing the fracture. It turns out that the correlation with mortality approaches the statistical significance thought to be due to headgear, especially in falls from a height or from a motorcyclist. The opposite mechanism is described: a pendulum force, causing more extensive than usual injuries, with massive hemorrhage from ruptured vessels.
Most often, pelvic fractures occur due to car accidents, collisions with pedestrians, collapses of buildings or earth, etc.
Symptoms of pelvic fractures complicated by damage to internal organs
In men, pelvic fractures often damage the urethra, less often the bladder. In this case, complete and incomplete ruptures occur, accompanied by complete or partial urinary retention. Often a drop of blood appears on the outer edge of the urethra. In the event that a complete rupture of the bladder has occurred, it is not possible to pass a catheter into it. The appearance of blood from the catheter is also a consequence of complete damage to the urethra. If bloody urine appears first, and then clean, then partial damage to the urethra is diagnosed.
Massive bleeding is often a complication of pelvic fractures. From here and any tactics to master them. One of them, used on an increasing scale, is catheterization and embolization of bleeding vessels. The Chinese authors also compared the results of conservative treatment with embolization in 39 patients with hemodynamic instability. Hemostasis reached an average of 2 hours. There was no intraoperative damage to vessels, nerves, or other organs; 3 patients experienced pain in the extremities, and 5 patients had transient ischemia without significant consequences.
Complications arising from pelvic fractures
In order to prevent some complications, mummy is used for fractures. All complications that arise due to fractures of the pelvic bones are divided into 3 main groups by specialists, and this depends on the time of their occurrence:
Fracture ischial bone care
The volume of fluid and blood transfusion, elimination time and mortality were significantly lower than in the conservative group. Arterial catheterization and embolization is a way to stop bleeding not only from pelvic fractures, but also from damage to the parenchyma, such as the liver or spleen, and even branches of the vertebral artery. Non-operative treatment of liver injury is now the rule rather than the exception, although it is still not successful in some cases. These patients require close attention.
- Direct consequences, i.e. those that occur directly at the time of the fracture.
- Early consequences (a few days after the fracture).
- Late consequences (long time after the fracture).
A systemic complication of a fracture can be hypovolemic shock, aseptic traumatic infection, with an open fracture - sepsis, a delay in fusion or incorrect fusion of bones, as well as nonunion.
In one abdominal embolism, another in angiography and embolization was performed after the initial conservative treatment, and in this case - liver necrosis in the area of embolization, the third - conservatively, and also effective in terms of hemorrhage. Angiography can help not only improve damaged vessels, but also restore their continuity. An example is an article by French authors. They described a case of traumatic kidney injury. The typical treatment in such cases is observation, often with removal of the kidney, sometimes surgical reconstruction of the artery.
Local complications are damage to the main blood vessels, muscles and tendons, traumatic compression syndrome and damage to internal organs, as well as local infection, osteomyelitis and osteoarthritis.
Very often, due to a fracture of the pelvic ring, a rupture of the bladder or urethra occurs. In this case, the patient needs urgent surgery.
Percutaneous angioplasty was used. Stents were introduced, giving an instant effect of 100%. Antithrombotic and antiplatelet treatment was started. In one case restenosis occurred and the patient was treated again. Ultimately, after a mean follow-up of 28.6 months, no additional complications were reported in the form of renal failure or hypertension. They are caused by high energy injuries and are accompanied by injuries to other areas of the body. Of those who die in the first hour after such an injury, 80% die due to massive hemorrhage.
The developed syndrome of traumatic compression can cause limb amputation.
With fractures of the posterior half ring, retroperitoneal hematomas occur, which are characterized by clinical picture acute abdomen. In this case, intrapelvic anesthesia is done to reduce the pseudo-abdominal syndrome.
As a rule, with adequate treatment, pelvic fractures heal well. However, if adjacent tissues were damaged during the fracture, the patient may limp for a long time due to the slow recovery of muscles and ligaments. Damage to the nervous tissue leads to chronic pain, as well as damage to some joints and sexual dysfunction. To prevent many problems, proper nutrition is required when bones are fractured.
When the fissure is unstable and hemodynamically unstable, external pelvic stabilization is required, done as soon as possible, preferably within the first hour of injury, and considered as one of the resuscitation procedures. Italian surgeons do this by placing the stabilizer in front. As a result of the operation, the volume of the pelvis decreases, and, consequently, the volume of the retroperitoneal hematoma, bleeding from the bone marrow decreases, limiting their mobility, thereby contributing to blood clotting. Stabilization also makes the patient more mobile for further examinations and possible actions.
Degrees of dysfunction of the body
I degree. there is no shortening of the limbs and atrophy of the gluteal muscles. In this case, there are no restrictions on the patient's life.
II degree. It is characterized by contracture hip joint. Pain syndrome, hypotrophy of the gluteal muscles and moderate restriction of movement are noted.
It is a quick and easy method for surgeons familiar with the subject and according to the Italian authors, an external stabilizer is the "gold standard" in these cases. It is also the ultimate cure. And it would be hard to disagree with this proposal, although the management of pelvic hemorrhage is also achieved by embolization, as well as by packaging.
They are caused by high energy trauma and are often associated with organ damage. For this reason, they require multidisciplinary treatment. The procedure is for early diagnosis and effective treatment most life threatening. Computed tomography can be successfully used to diagnose bone disorders. It has long been used in a 3D version to evaluate not only pelvic fractures but also spine fractures, which can be useful in diagnosing injuries. chest, as well as fractures of the limbs, especially when it comes to joints.
III degree. The function of the hip joint is very limited, the gluteal and thigh muscles are atrophied, the patient has a duck gait.
Treatment of a clavicle fracture in children
Fracture of the collarbone is one of the most common injuries in children 2 - 4 years of age. It occupies a leading position in the ranking of fractures after the forearm and shoulder. A direct fracture of the clavicle occurs as a result of its direct impact, however, such a condition in life is quite rare. Much more often, an indirect fracture of the clavicle occurs when it breaks due to a blow from the shoulder, a fall on the elbow or outstretched arm, and also with simultaneous strong and sharp compression of the shoulder joints.
The authors reported 28 patients with severe acute pelvic trauma and hematocrit. All 120 ml of Blink are given in a bolus. Fracture of long bones as a result of multiple injuries. Early definitive stabilization generally refers to the selection of large bone fractures in patients with multiple injuries. Some modifications are necessary when the condition of these patients is critical or when other injuries dictate a different delivery order. The time and type of treatment and complications were analyzed.
The gender distribution was almost the same, the German patients were slightly younger but slightly worse. In both groups, the time from accident to surgery was not too short. On the contrary, more intensive treatment in Germany did not lead to better results. Only this is the case with the final proceedings, and, as the article says, this does not concern the group of the most affected people.
Injuries incompatible with life
Emergency physicians and emergency medicine centers deal daily with victims of injuries of varying severity. Patients with mild to moderate injuries may be treated on an outpatient basis or in specialized department hospital. Victims with severe injuries are in intensive care units, and sometimes they do not even have time to get to the hospital.
As injury control in orthopedics, the least traumatic procedure has been identified to reduce the inflammatory response, however, resulting in rapid stabilization of bone injury. The answer to the question of what benefits and how safe such tactics are is obvious, although the authors refrain from definitively resolving this problem in patients with injuries of the central nervous system. More or less, this question applies to other fractures, including vertebral fractures. Based on a review of the literature on this topic, 11 articles were selected over the past 20 years that directly compare the outcomes of early and delayed treatment of vertebral fractures.
Damage to the hip joint and pelvic bones is a dangerous injury associated with loss of mobility and severe limitation in movement. It can lead to complete paralysis of the lower extremities, its consequences can cause disability. The pelvis has a complex structure. One of its main components is the pubic (or pubic) bone, consisting of 3 parts - the main body and located on both sides of the branches. There are injuries, depending on the presence or absence of the integrity of the pelvic ring.
Based on this, the authors found that it is almost certain that the early stabilization of these fractures leads to more short terms hospitalization, reduced respirator treatment time, fewer complications including pulmonary complications, and better neurological outcomes. Therefore, the Italian authors, following the fear of complications associated with intramedullary nailing, adopted the tactic of injury control by securing these fractures using an external Sheffield ring stabilizer in the case of open multiple femoral fractures.
A fracture of the pubic bone of the pelvis refers to the type of damage that does not violate the integrity of the pelvis itself, the injury is the result of a blow of great force, directed directly to the center of the main bone or with increased indentation. At the same time, the bones are not subject to displacement, and the severity of the injury is determined by the location and size of the damage. Athletes and elderly people with serious diseases associated with a violation of the structure of bone tissue (osteoporosis) are often susceptible to a fracture of the pubic bone. Injury occurs when the muscles around the bone contract violently.
The duration of stabilizer treatment averaged 7 months, and an average of 3 years of follow-up was found in all cases of bone marrow, excellent limb function. Thus, in their opinion, by avoiding the "second hit" phenomenon, an early start of patients and healing of primary bone defects are obtained by using multidirectional stretching without the need for re-treatment.
Similar requests came to the Norwegians. In 30 rats, they performed an osteotomy of the tibia and provided it with an external stabilizer. After 7 days, 10 stabilizers were removed and diluted and 10 thick intramedullary nails were removed. 10 left. The results of fracture healing were similar in all groups. Secondary orthopedic surgery can be anything but revealing. Against this background, one cannot ignore that intramedullary nail fractures have become the “gold standard” for the treatment of femoral fractures.
To determine the methodology and mechanisms of treatment, it is important for a doctor to know the cause and nature of the damage received. Common causes of injury:
- accidents and collisions with pedestrians;
- direct blows;
- landslides of rocks and soil rocks;
- falling from height;
- getting into squeezing conditions (between cars, wagons, etc.).
A fracture of the pubic bone can be either spontaneous or with complications combined with cracks and violations of the structure and integrity of other pelvic bones. It can, in some cases, cause ruptures in the internal organs located in the pelvis (female genitals, bladder, rectum).
Symptoms

Signs of injury to the pubic joint are:
- acute pain in the injured area with minimal movements, it is characteristic of almost all pelvic injuries;
- subcutaneous hemorrhages;
- puffiness;
- numbness of the place, observed in violation of the integrity of the nerve trunks;
- limited movement, inability to raise the leg (the effect of a stuck heel);
- hematoma and induration, hardening of the impact site.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing an injury, it is important for a doctor to:
- medical history indicating the nature of the injury;
- patient complaints;
- examination indications;
- additional diagnostic tools (if necessary).
The most commonly used diagnostic method is radiography. In this case, an overview image is taken, as well as, for accurate diagnosis and correct diagnosis, an aiming photo of the pubic (pubic) bone.
First aid
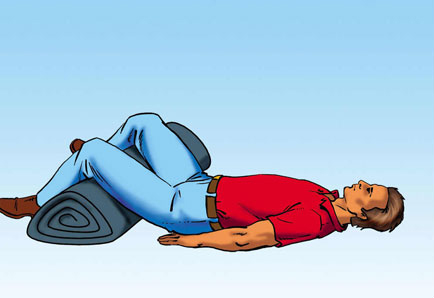
In case of a fracture of the branches of the pubic bone, the speed and quality of emergency care are important, which can subsequently become a good factor and indicator for further treatment and complete recovery of the patient. Before starting its implementation, it is necessary to call a doctor and, while waiting for his arrival, provide assistance to the victim.
In this case, immobilization of the injured person is important so that the resulting fragments do not move and this does not lead to damage to their edges of soft tissues or internal organs. For this, the patient is laid on his back and a roller or an object replacing it is placed under his knees.
The patient needs pain relief, for this, drugs with a strong effect, both general and local, are used. Serious attention is paid to the elimination of pain shock, from which the patient may lose consciousness, therefore, before the arrival of doctors, it is necessary to pay attention to the general condition of the injured person - to his pulse and heart rate.
In severe open injury, with wounds and soft tissue damage, it is necessary to use disinfectants process them and cover with a cloth, protecting them from bacteria and infections. With abundant blood loss, it is necessary, if possible, to apply a tourniquet or tightly close the place of rupture of blood vessels.
Treatment
Then the patient must be placed in a hospital where the necessary treatment is carried out. Correct diagnosis is important, which will determine the severity and specific location of the lesion. This will reveal the facts of damage or their absence in the internal organs. In case of large blood loss from soft tissue injuries or ruptures in the internal organs, a transfusion of donor blood or plasma may be recommended to the patient.
Damage to the pubic bone or fracture of its upper branch, depending on the severity, requires conservative treatment or surgical intervention. The operation is necessary for a patient who has a large number of small fragments of bone tissue that cannot be compared into a dense structure. Through the incision made, they are removed.
The patient may need surgery when diagnosing damage to the internal organs of the small pelvis, which are manifested by the following symptoms:
- urination with blood fragments;
- urinary incontinence;
- bowel problems, etc.
Their detection is possible with the help of ultrasound, MRI and other diagnostic procedures and methods.
Rehabilitation
Complicated fractures are quite difficult. They are multiple and are accompanied by damage to the joints and bones of the pelvic ring, blood vessels, nerve endings and internal organs. Their most common localization is the anterior pelvis. Depending on the severity of the injury, there are three stages in the restoration of the functions of the pelvic bones. The appointment of a complex of recreational activities and therapeutic exercises is carried out by a rehabilitation doctor.
At the first stage, the specialist faces the following tasks:
- restore the work of internal organs;
- prevent muscle atrophy;
- promote relaxation of muscle tone;
- gradually restore the functions and work of the lower extremities.
At the second stage, supplemented by small physical activity, the patient is prepared for standing and the first steps, in connection with this, muscles and joints are developed. At this stage, the sitting position does not apply.
The third stage is marked by gradual loads and exercises that promote rotation of the torso, bending of the legs; in case of injury to the pubic joint, squats with the bent legs apart are included in the complex.
With complex fractures, from the first to the last stage, all loads are assigned and performed under the close supervision of a specialist.
Massage promotes recovery at all stages. It allows you to normalize the work of impaired blood circulation and prevent muscle atrophy of a bedridden patient.
Consequences
Untimely access to a medical facility in case of pelvic injury can lead to unpleasant consequences and complications:
- damage to the pelvic muscles, nerve trunks;
- formation of prerequisites for the appearance of osteomyelitis, osteoarthritis;
- traumatic blood loss;
- disruption of the pelvic organs;
- the formation of infectious and inflammatory processes (internal and external);
- incorrect fusion of bone tissue;
- the appearance of growths;
- thinning of muscle fibers that limit motor activity;
- lameness, etc.
In some episodes, patients notice a decrease in the length of one limb, which leads to a violation of the proportions of the human body, there is a suspension of bone fusion, partial or complete loss of mobility.
Pelvic injury and its consequences are serious and dangerous injuries. musculoskeletal system person. You need to take its treatment seriously and remember that the quality of your future life depends on it.