The extraction of wisdom teeth is carried out by a dental surgeon, and it does not matter where they are located, on the upper or lower jaw. Compared to upper molars, it is much more difficult to remove eights from below, since the jaw is anatomically denser in this area. The consequences on the lower jaw can be different, because after any operation there is a risk of complications, and extraction is no exception.
Of course, on empty place they will not arise, for this you need good reasons. But influence the course postoperative period may be the method of removal, how responsibly the patient complies with the doctor's instructions, the professionalism of the doctor, the compliance of the manipulation with technological standards.
In practice, it has been established that after the removal of a tooth from the upper jaw, the consequences occur much less frequently, since the molar is extracted in a simple, less traumatic way.
Wisdom teeth are located at the very end of the jaw, which makes it difficult to properly care for them and complicates the full treatment. By general criteria, the removal procedure is a laborious process, which is equivalent to a minor surgical intervention.
If there are no significant obstacles and risks of complications, the dentist will always try to cure his own tooth, because you can always get rid of it. But unfortunately, in practice this happens extremely rarely due to the "unpredictability" of the third molars.
They are the last to erupt at a conscious stage of life (17–25 years) and at the same time bring a lot of weight to a person. discomfort. And this is due to the anatomical properties, which cause a lot of trouble, so often wisdom teeth have to be removed.
Indications for extraction of wisdom teeth:
- Pericoronitis. Initially, the gum hood is excised to facilitate the germination of the eight and eliminate purulent accumulations. In case of recurrence, the tooth must be removed;
- Incorrect location of bone tissue, change in the angle of rotation of the tooth, oblique placement. This factor is an absolute indication for removal, since it is absolutely of no value, but only becomes a source of problems for the patient and the entire dentition.
- Deformities of the tooth, abnormal shape, the presence of curved roots;
- There is not enough space on the jaw for the full growth of the wisdom tooth. If such a molar is left, then in the future it will lead to displacement of the remaining teeth, crowding and other consequences.
Possible consequences
There is always a possibility of complications after the removal of a wisdom tooth, so you should not think that the removed molar will immediately relieve all problems. On the contrary, after removal, a new critical stage begins - the healing of the wound surface and the restoration of damaged tissues, and its full cycle takes about six months.
Particular care of the patient is required during the first two weeks after surgery. It is necessary to carefully care for the oral cavity, properly treat the wound, and maintain the integrity of the blood clot.
As I testify to practical examples, the person himself becomes the main culprit of the consequences, of course, unintentionally, but because of his own inattention.
In addition, the individual susceptibility of the body is far from the last place, one person is easily rehabilitated, while the other may face a full range of unpleasant sensations. Among them are post-traumatic factors in the form of physiological pain, swelling, bleeding from the hole.
Below we will consider the most common complications and consequences that people face by removing wisdom teeth from both the lower and jaw.
The appearance of pain
When, under the influence of an anesthetic, a wisdom tooth is removed in the upper jaw, the consequences often manifest themselves in the form of pain (the situation is similar for the teeth of the lower row). After the influence of the anesthetic stops, soreness appears, which is a physiological reaction to injury.
The level of the syndrome directly depends on the complexity of surgical measures, respectively, the more tissues were destroyed, the stronger the post-traumatic pain. It is better to prepare for such sensations in advance, especially for sensitive people.
Soon, the unpleasant symptoms will pass, and in order to alleviate the condition, it is not forbidden to take painkillers or powders, just do not exceed the dosage indicated in the instructions. That is, to drink medicine without fanaticism, strictly as needed.
Bleeding from hole
For the first time in a day, you don’t need to be afraid of bleeding - this is also considered a variant of the norm and a natural process that promotes speedy healing. But it is necessary to monitor the condition, the next day the bleeding should stop completely, if the reverse picture is observed, then you should go to the doctor, because excessive blood loss can cause drowsiness, fainting, weakness.
It is worth noting that bleeding can be stopped by lightly pressing with a sterile swab, but you can not diligently press on the hole or try to clean the blood. Such actions will lead to a "dry socket", which will entail an inflammatory process and alveolitis.
![]()
A blood clot at the site of the removed G8.
Temperature rise
An increase in temperature to 38 C for 1-2 days after the removal of wisdom teeth is due to the activation of the immune system to protect the body, so this sign should not be alarming, except when the temperature is stable.
Under such circumstances, this will already be a reaction to the development of the inflammatory process, so it cannot be recklessly knocked down, it is necessary to go to the dentist urgently.
The consequences after the removal of a wisdom tooth in the form of the development of alveolitis are quite common. This complication is no longer a variant of the norm, but a pathology, the resolution of which follows in the dental office.
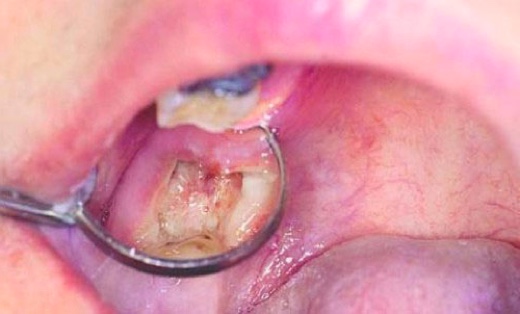
Alveolitis develops for the following reasons:
- the doctor acted too traumatically during difficult removal, which caused significant tissue damage;
- the eight was affected by caries and its fragments were in the wound;
- dry socket syndrome - this indicates the loss of a blood clot. It can become such due to the patient's ignorance regarding the correct care of the wound surface. A person independently removed a clot out of ignorance, washed it during hygiene or rinsing, took it out with a tongue or a toothbrush;
- poor oral care, ignoring brushing your teeth, non-compliance with the recommendations of the doctor.
Alveolitis is accompanied by suppuration in the hole and makes itself felt by soreness, chewing discomfort, edema, swelling, high temperature, the appearance of a smell of rot from the mouth.
If you find such signs, you should not waste time on an independent solution to the problem. Only qualified medical assistance will help prevent the development of osteomyelitis, phlegmon, lymphadenitis, abscesses.
Bruising
When a wisdom tooth is removed in the lower jaw, the consequences in the form of a hematoma (bruise) occur very often. They appear under the following circumstances:
- a vessel ruptured due to inaccurate injection of an anesthetic;
- high blood pressure;
- capillaries are vulnerable to damage.
Even if the upper or lower jaw has acquired a bluish tint, this is not a cause for concern. You just need to wait a few days until the consequence in the form of a cosmetic defect resolves itself.
And in order to prevent swelling of the face, the appearance of hematomas, it is very useful to regularly apply cold to the operated area. This simple method works flawlessly.
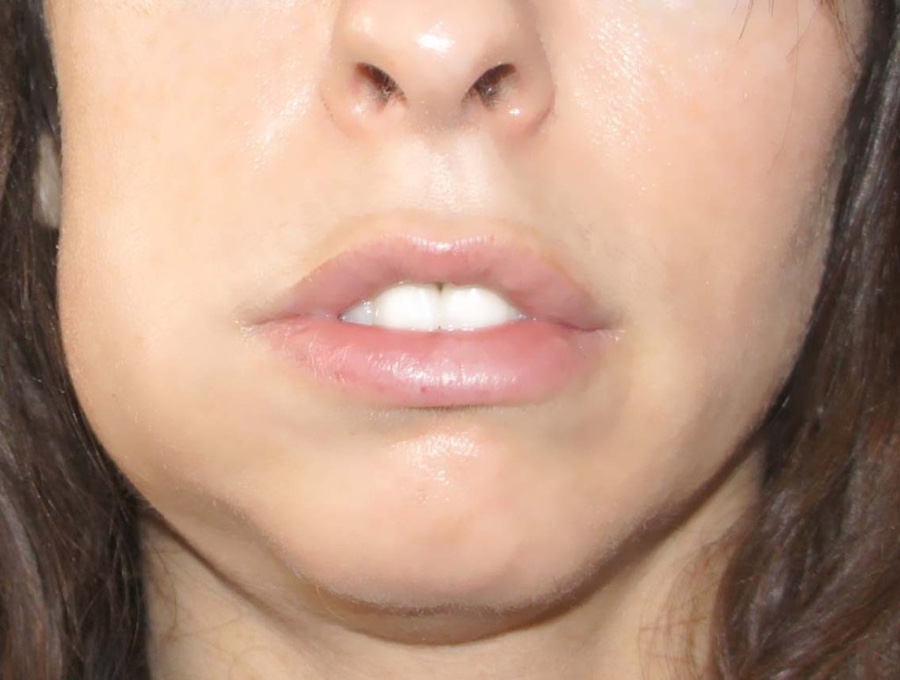
This is what a swollen cheek looks like. The swelling may be less or much more.
Loss of sensation
Some experience paresthesia, which is characterized by a temporary loss of sensation. Perhaps numbness of the lips, facial area, cheeks, chin, tongue. Paresthesia does not appear for no reason and does not belong to normal conditions, but indicates that the mandibular nerve, located next to the third molars, has been injured.
Factors that increase the likelihood of paresthesia, as a consequence of the extraction of wisdom teeth:
- features of the location of the dental roots, the presence of an inflammatory process. In some people, tooth roots are located near the nerves, which can cause loss of sensation;
- unprofessional surgeon, incorrectly compiled surgery, especially if the doctor did not see the need for x-rays.
Only isolated examples are known when sensitivity never returned to a person. These effects of wisdom tooth removal disappear after 1-2 weeks. The patient is shown taking special drugs, physiotherapy procedures.
You can watch the video below personal experience author:
Features of the operation
Before deciding on an extraction, the patient must undergo an X-ray examination, which allows a full assessment of the condition of the third molars, the results will become the determining factors for choosing the extraction technique.
To pull out a wisdom tooth that does not have any special deviations from the established norms, the doctor resorts to a simple extraction. For this, only forceps are needed, with which he simply fixes the crown of the figure eight, loosens it, and then pulls it out. The whole process takes no more than 15 minutes, while the surrounding tissues remain as intact as possible.
Basically, this method is used if it is necessary to remove a tooth from the upper jaw, since it has a porous structure. As for the manipulations on the dense lower jaw, then all actions take place according to a complicated version, especially if the wisdom tooth appeared partially, did not erupt at all, has a lot of anatomical deviations (it lies incorrectly, crooked roots), which further aggravates the picture.
Sometimes there are situations in which tooth extraction is required. The consequences of surgical intervention will not be long in coming. They can be very different - natural (caused by the operation), individual (associated with the personal physical characteristics of the body), abnormal (when something starts to go wrong).
What is tooth extraction?
Tooth extraction is a simple, but unpleasant process. It is associated with the patient's expectation of pain (most often, false, since modern anesthetic drugs easily cope with the function of anesthesia), and with psychological unwillingness to lose one of the necessary elements of the body.
The extraction itself is fast. The dentist-surgeon carefully removes the tooth from the socket of the alveolar jaw process with special tools. In particularly difficult cases, incisions can be made on the gums and sutures are applied. Extraction of a multi-rooted tooth can be done in parts.
What should be prepared immediately after the operation?
What to do after tooth extraction? First of all, take it seriously! Seemingly simple at first glance, this operation in practice is a real stress for the body. Therefore, in the first 72 hours, it is advisable to refrain from physical and psychological stress.
Having removed the tooth, the dentist either sews up the wound or puts sponges that stop the blood in the hole. They adhere strongly to the mucosa and dissolve over time. Following the sponges, a cotton-gauze swab is placed on the damaged area. With his pressure, he presses the lips to the mucosa and promotes rapid healing wounds. The tampon is removed from the mouth no earlier than half an hour to an hour after the operation. You can start eating in a few hours.
As soon as the effect of anesthesia ends, the disturbed tooth socket begins to hurt - and not just severely, but unbearably severely.--noindex-->
In this case, it is necessary to have painkillers on hand - for example, Ketanov. The dentist must prescribe pain-relieving medications for each patient.
What kind of lifestyle to lead at first?
In the first days after tooth extraction, avoid hot, spicy and hard foods, as well as alcohol and any hot drinks. The affected side should not be heated, it should not be eaten or rinsed intensively.
Water can wash out the blood clot that has formed in the socket and either open the wound again or lead to the formation of a dry socket.
You can brush your teeth a day after the operation, provided that this is in principle possible. Usually, after tooth extraction, the gum hurts: it swells a lot and interferes with both normal chewing of food and home hygiene procedures. The postoperative tumor subsides in the first hours, less often - a day after tooth extraction.
The main consequences of tooth extraction
Among the natural, reaching the level of individual, the consequences of tooth extraction include:
- Bleeding that lasts no more than half an hour under the most favorable conditions, eight hours is normal and 72 hours in patients with low blood clotting. The release of a large amount of blood after a few hours is considered a pathology and requires examination by a dentist.
- Severe pain that disappears after taking one or two painkillers within a few hours, and weak - in the next three days.
- Severe swelling of the gums and cheeks in the first 24 hours and light in the next 48 hours after tooth extraction.
- An increase in body temperature to 37.5 - 37.8 degrees in the first days. In individual cases, the temperature can be kept for seven to eight days.
- Reduced immunity and the appearance of mild signs of a cold in people with poor health.
Many patients ask themselves: “What to do to avoid possible complications after tooth extraction, how to rinse your mouth and is it possible to do this? The answer to this question is simple: it is best to turn to natural remedies - warm tinctures of chamomile or sage. They perfectly relieve inflammation and disinfect the mucosa.
Complications after tooth extraction
Among the unnatural, requiring additional dental intervention, the consequences of tooth extraction include:
- Dry socket resulting from the loss of a blood clot. Gum healing is carried out by means of tissue-restoring ointments after consultation with a doctor.
- Suppuration of the hole, which occurs due to poor personal hygiene or improper tooth extraction. The problem with what to do if the tooth socket is inflamed is also solved by the attending dentist.
- Paresthesia - numbness of the tongue, lips, in rare cases - the chin, due to damage to the facial nerves. It usually happens when wisdom teeth are removed. It goes away within one to two weeks.
Removal of a tooth, or exodontia, has been known since ancient times. In fact, teeth were pulled out not only to relieve suffering from toothache, but also with more bloodthirsty goals - for intimidation and torture.
However, for centuries, exodontia was hardly the only way to solve dental problems. And before the invention of antibiotics and the development of adequate tools, this method, even with the best intentions, was not only painful, but also dangerous - people fell ill and died due to unsuccessful tooth extraction.
In the 14th century, the advanced medieval surgeon Guy de Chauliac first used the "tooth pelican" - a device that allowed more or less accurately and quickly "uproot" the tooth along with the root. "Pelican" was used with success until the 18th century, until it gave way to more modern equipment. Today for tooth extraction different tools and techniques are used, depending on the specifics of the situation.
Contemporary removal of a tooth- an operation that is responsible and difficult not only for the patient, but also for the dentist. They resort to the removal of a molar tooth only if there are irrefutable indications: if the tooth cannot be saved (or there is actually nothing to save), if its condition threatens the “neighbors in the jaw” or threatens with complications, inflammation, infection. In some difficult cases removal of a tooth becomes a necessary part of orthodontic procedures related to bite correction. In a word, tooth extraction is an extreme measure that is resorted to if it is impossible to solve the problem in another way.
The main reasons for tooth extraction:
Infection or extensive damage to the tooth by caries (about 2/3 of all extractions!)
- the tooth interferes with the normal growth of other teeth
- some gum disease that has spread to other tissues and disrupts the integrity of the jawbone
- the tooth is broken off or significantly destroyed (due to an accident, fight, etc.)
- a wisdom tooth often becomes a candidate for removal even without pain and other symptoms, since it can change the symmetry of the face or change the bite, as well as “suppress” neighboring teeth.
There are two main types tooth extraction: simple and surgical. A simple extraction involves extracting a visible tooth from the jaw. It is performed under local anesthesia (injection) and, as a rule, only instruments that lift and pull the tooth are used during it. The tooth loosens slightly to disrupt the integrity of the periodontal tissues, the alveolar bone supporting it expands, and, applying forceps, the doctor pulls the tooth out of the jaw.
Surgical removal is used for tooth extraction, access to which is difficult - for example, if its crown ( top part, visible above the gum) is broken off, or it has not completely erupted. In each case, the dentist chooses his own strategy for tooth extraction - only soft tissues or it becomes necessary to remove or dissect part of the jawbone. IN difficult situations The tooth is crushed and removed piece by piece.
What to do after tooth extraction?
So, for whatever reason, you have lost one of your thirty-two little friends. How to survive the loss with the least loss for nerves and health?
While you are still in the clinic, do not jump up immediately after the doctor has finished working and showed you the extracted tooth. Too sharp a burst of physical activity can lead to bleeding - it takes some time for the blood to thicken and, under the influence of oxygen, a thicker “plug” forms in the jaw, covering a fresh wound. If you had a simple removal - you need at least 10 minutes of rest, in case of surgery (especially if stitches were applied), you should sit quietly for 30-60 minutes. Your doctor may suggest that you bite down on a gauze pad. Don't give up, jaw pressure will also help stop the bleeding.
Before you go home, the dentist will schedule a follow-up appointment for you and list the procedures for post-operative oral care, prescribe the necessary medications. Follow all instructions carefully. For at least two hours after a tooth extraction, refrain from sudden movements, do not touch the wound with your tongue or hands, do not chew gum and do not suck on sweets or tablets, this can provoke or increase bleeding.
A small amount of red blood will continue to flow for some time, this is normal. If the bleeding gets worse and clots appear, bite down on a piece of gauze or a rolled-up piece of paper towel, trying to maintain pressure for 40-50 minutes straight. If bleeding continues to bother you, call your dentist or go to a clinic. Bleeding usually resolves within 8 hours after tooth extraction, in some cases, the release of blood in the period of 72 hours after the operation can be recognized as a variant of the norm.
In case of pain attacks, take the remedy recommended by your doctor. It is best to avoid aspirin and aspirin-containing drugs, as they thin the blood and keep it from stopping. Most likely, the dentist will advise you to take an ibuprofen tablet.
It is extremely important to keep the surgical site clean, especially if you have undergone surgical removal, removal of a tooth wisdom. Be extremely careful when brushing your teeth and, unless the doctor prescribes otherwise, gently rinse the mouth (not the hole!) With a tepid saline solution (half a spoonful of salt per glass of water) or a solution of chlorophyllipt (10 drops per 100 ml of water). Make sure that no food particles get into the wound. On the day after tooth extraction, take only homogeneous food, gradually returning to the usual menu. Until complete recovery, refuse to visit the bath, sauna, hot baths.
Possible complications after tooth extraction
Like any surgical intervention, removal of a tooth may not go as smoothly as we would like. TO possible consequences include, in addition to bleeding, swelling, fever, infection.
In contrast to the Middle Ages, today infection and inflammation accompany tooth extraction extremely rarely, but such cases are recorded from time to time. First, you need to make sure that the infection and inflammation are not related to the fact that some fragment of the tooth or instrument is “forgotten” in the jaw. Secondly, it is necessary to start antibiotic treatment as soon as possible. Therefore, at the slightest sign of infection (suppuration, severe pain), consult a doctor immediately. If you had a wisdom tooth removed and by the end of the week after surgery, your mouth does not open wider, this may also be a sign of infection.
Edema - very common consequences of tooth extraction especially a wisdom tooth or a severely rotten tooth. Swelling of the gums and cheeks after removal is caused by partial destruction of the soft tissues surrounding the tooth. As a rule, such annoying, but relatively small, flux-like edema disappears on its own after 2-3 days, facial symmetry and diction are restored.
Also, swelling can be caused by an allergic reaction to the drug used for anesthesia - then an antihistamine will help. Worsening, painful, throbbing, and hot swelling after tooth extraction may be a sign of an onset of infectious inflammation. In this case, you should immediately contact the clinic and in no case self-medicate.
Increased body temperature after tooth extraction is the body's normal response to injury. The temperature can "jump" for 2-3 days, normalizing in the morning and rising in the evening, this in itself does not mean infection. Follow the prescribed hygiene and take antipyretics (paracetamol and ibuprofen), but if the condition does not improve on the fourth day and you also do not like the condition of the wound, this is a good reason to visit a doctor.
Contraindications for tooth extraction
Postpone removal of a tooth if you are menstruating or if you are pregnant (first and third trimesters). In the first case, removal is fraught with severe bleeding, in addition, in most women, for hormonal reasons, the pain threshold is underestimated. In the second, the use of anesthesia can adversely affect the fetus, as well as inevitable stressful experiences. If you suffer from diseases of the circulatory system or take cardiac medications, be sure to inform the dentist - this may also serve as a reason for a medical withdrawal.
Olga Chern
Women's magazine JustLady