It is formed by a bone base (pelvic bones), muscles (pelvic muscles) and filled with internal organs (pelvic cavity organs).
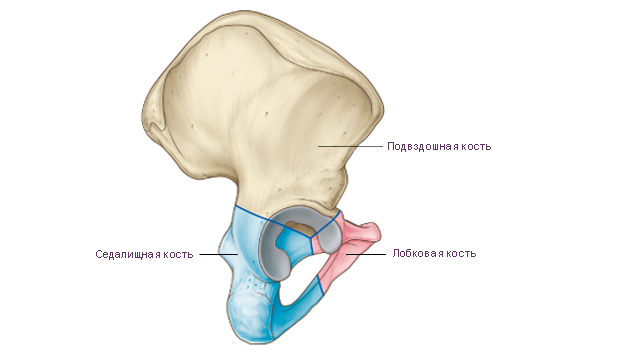
Pelvic bone The adult human consists of three fused bones: the ilium, the pubis, and the ischium. Before the age of 12–16, these individual bones are connected by cartilage. The place of fusion of the bodies of these bones is the deep acetabulum. It is the articular fossa for the head of the femur. The acetabulum has a high edge around its circumference. On its medial side is located acetabular notch. For articulation with the head of the femur in the acetabulum, along its periphery, there is a semilunar surface. In the center of the acetabulum is acetabular fossa.
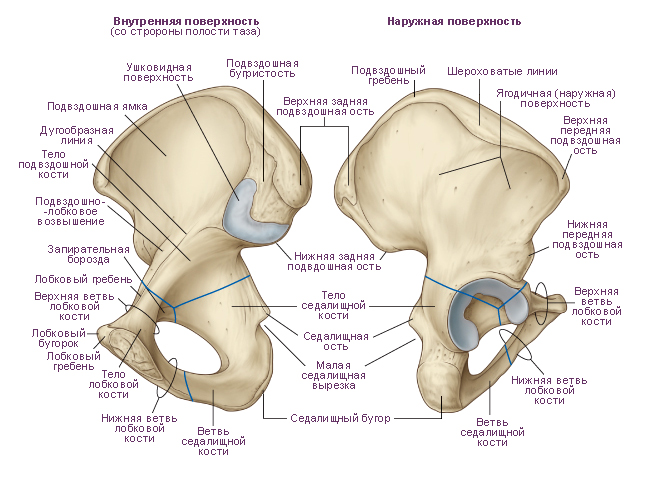
Ilium consists of two departments. The lower thickened section is called body ilium
. The body participates in the formation of the acetabulum. The upper expanded section is called wing of the ilium. The wing is a wide curved plate, thinned in the center. At the periphery, the wing is thickened, fan-shaped, and ends iliac crest. Three visible on the iliac crest rough lines for attachment of the broad abdominal muscles. These formations are called: outer lip, inner lip and intermediate line. The iliac crest has bony protrusions at the front and back. The protrusions located at the front are called superior anterior iliac spine And inferior anterior iliac spine. The protrusions located at the back are called superior posterior iliac spine And inferior posterior iliac spine.
On the outer surface of the iliac wing, three faint rough lines can be seen, where the gluteal muscles and the fascia covering them begin. Anterior gluteal line the longest. It begins near the superior anterior iliac spine and runs in an arched direction towards the greater sciatic notch of the ischium. Posterior gluteal line located almost vertically and parallel to the posterior section of the previous line. Lower gluteal line shorter than others. It begins between the superior and inferior anterior iliac spines and runs above the acetabulum to the greater sciatic notch.
There is a flat depression on the inner surface of the ilium wing. They call him iliac fossa. The inferior border of the iliac fossa is arcuate line. The arcuate line reaches behind the anterior edge auricular surface. This surface serves for articulation with the corresponding surface of the sacrum. The arcuate line continues anteriorly into the iliopubic eminence. Above the auricular surface is iliac tuberosity for attachment of interosseous ligaments.
pubic bone has an expanded part - the body, and two branches. Body of the pubis forms the anterior part of the acetabulum. Goes from the body anteriorly superior ramus of the pubis With iliopubic eminence, located along the line of fusion of the pubic bone with ilium. The anterior part of the upper branch bends sharply downwards and passes into inferior ramus of the pubis. In the area of the medial edge of the pubic bone there is an oval shape symphyseal surface. It serves to connect with the paired pubic bone of the opposite side. On the superior ramus of the pubis, near its medial end, there is pubic tubercle. Runs along the posterior surface of the lower branch of the pubic bone in the direction from back to front and medially obturator groove. Blood vessels and a nerve of the same name pass through it.
Ischium has a thickened body. Body of the ischium complements the acetabulum from below and anteriorly passes into branch of the ischium. The body of the ischium with its branch forms an angle open anteriorly. In the region of this angle, the ischium has a thickening - ischial tuberosity. Above the ischial tuberosity, the ischial bone extends from the posterior edge of the body ischial spine. The ischial spine separates two notches: the inferior lesser sciatic notch and top greater sciatic notch. The ramus of the ischium connects to the inferior ramus of the pubis. This connection closes at the bottom of an oval shape obturator foramen.
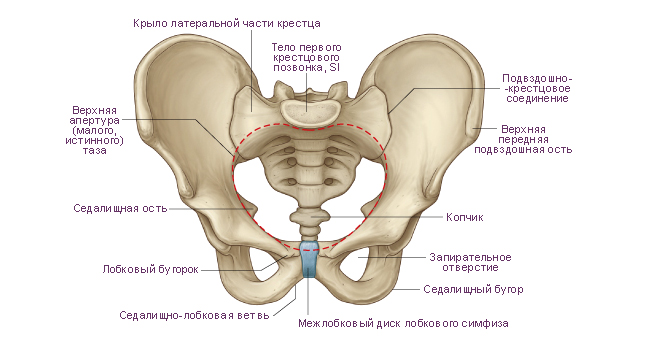
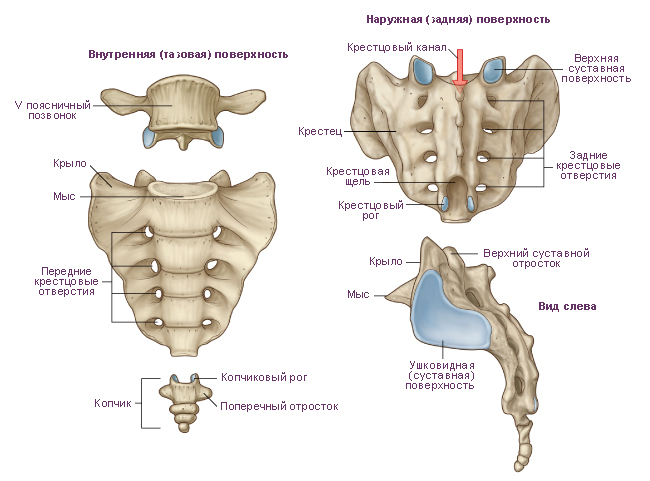
Sacrum consists of five sacral vertebrae. These vertebrae fuse into one bone during adolescence. The sacrum has triangular shape. It is a massive bone and bears the weight of almost the entire body. The following structures of the sacrum are distinguished: base of the sacrum, apex of the sacrum, pelvic (inner) surface of the sacrum And dorsal (outer) surface of the sacrum. The base of the sacrum, with the help of articular processes, is connected to the lower articular processes of the V lumbar vertebra. In the area of connection of the base with the V lumbar vertebra, a rounded corner protrudes forward - promontory of the sacrum. On the concave pelvic surface facing forward, four transverse lines. These are traces of fusion of the bodies of the sacral vertebrae with each other. On each side at the level of these lines there are pelvic sacral openings. On the convex dorsal surface of the sacrum visible on each side dorsal sacral foramina. As a result of the fusion of the processes of the sacral vertebrae, five longitudinal ridges were formed. Unpaired median sacral ridge- these are fused spinous processes of the sacral vertebrae. Doubles intermediate ridge is the result of fusion of the articular processes of the sacral vertebrae, and the paired lateral sacral ridge formed during fusion of the transverse processes of the sacral vertebrae.
On the superolateral parts of the sacrum there are ear-shaped surfaces for articulation with the surfaces of the iliac bones of the same name. On each side between the auricular surface and the lateral ridge there is sacral tuberosity, to which ligaments and muscles are attached. The vertebral foramina of the fused sacral vertebrae form sacral canal. This channel below opens sacral fissure. The gap is limited on the sides sacral horns, which are rudiments of articular processes.
Coccyx consists of 3-5 vestigial coccygeal vertebrae. The coccygeal vertebrae in childhood are connected by layers of cartilaginous tissue. These vertebrae fuse into one bone during adolescence. The coccyx has the shape of a triangle curved anteriorly. The base of the coccyx is directed upward, the apex is directed downward and forward. For articulation with the sacrum there are coccygeal horns, corresponding to the sacral horns. At a young age, especially in women, the coccygeal vertebrae are connected by layers cartilage tissue.
|
Scheme. Superior pelvic aperture. |
|
 |
|
|
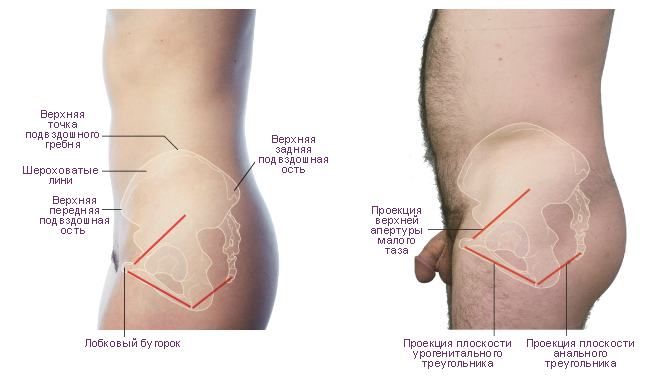
Scheme. Features of the position of the pelvis in the torso of a man and a woman. Left view. |
|
 |
|
|
Scheme. Pelvic bone. |
|
 |
|
|
Scheme. Sacrum and coccyx. |
|
 |
|
|
Scheme. Right pelvic bone. |
|
|
|
|
Premise: |
The ilium, os ilium, is the largest of the bones that form the pelvic bone. The lower part of the bone is thickened and is called the body of the ilium, corpus ossis ilii. The body of the bone forms the upper part of the acetabulum. On the inner surface of the body there is an arched line, linea arcuata, above which there is a wide, flattened part of the bone called the wing of the ilium, ala ossis ilii. The lower part of the wing, adjacent to the body, is narrowed, the upper part is wide. Its edge is somewhat thickened and serves as a place for attachment of muscles, the trace of which remains on the bone in the form of three rough lines, or lips: the outer lip. liabium externum. the inner lip, labium internum, and the intermediate line between them, linea intermedia.
In general, the upper peripheral edge of the wing is called iliac crest. Christa Iliaca. It is S-shaped and ends in front with a protrusion that can be easily palpated through the skin, which is called the superior anterior iliac spine, spina iliaca anterior superior, in the back - the superior posterior iliac spine, spina iliaca posterior superior. The anterior edge of the wing below the spina iliaca anterior superior has an iliac, or semilunar, notch, which is limited at the bottom by the lower anterior iliac spine, spina iliaca anterior inferior. Below it, the edge of the bone turns anteriorly and reaches the iliopubic eminence, eminentia iliopubica, which is the site of fusion of the body of the ilium with the pubic bone.
The posterior edge of the wing below the spina iliaca posterior superior bears the lower posterior iliac spine, spina iliaca posterior inferior, where the greater sciatic notch, incisura ischiadica major, begins, in the formation of which the body of the ischium participates. The outer surface of the wing of the ilium - the gluteal surface, facies glutea, bears a trace of the gluteal muscles that begin here - three gluteal lines: posterior, anterior and inferior. The posterior gluteal line, tinea glutea posterior, is located in front of the spina iliaca posterior superior and runs from the outer lip of the iliac crest to the base of the inferior posterior iliac spine.
The anterior gluteal line, linea glutea anterior, starts from the superior anterior iliac spine and, going backward, curves downwards in an arcuate manner, reaching the upper edge of the greater sciatic notch. The lower gluteal line, linea glutea inferior, is located above the upper edge of the acetabulum. The inner surface of the wing of the ilium in the anterior sections is smooth, slightly deepened and is called the iliac fossa, fossa iliaca. Its lower edge is limited by an arcuate line.
In the posterior part of the inner surface of the wing, above the greater sciatic notch, there is an articular ear-shaped surface, facies auricularis. In front and below it is limited by the periarticular groove. Posterior and superior to the auricular surface is the iliac tuberosity, tuberositas iliaca.
It is one of the parts of the posterior wall of the abdomen and has the shape of a depression. Its upper border is the ilium, in particular its crest, the anterior border is the beginning of the bone and ligament, the internal border is the connection with the sacrum, the lower border is the innominate line. In this case, the PC acts as the skeleton of this area, to which the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall are attached. Together, muscles and bones form a dense sheath.
Thus, the greater iliac bones are attached to the sacrum on both sides, which have rounded tops, so they can be easily palpated on the human body.
The ilium is the largest of all the bones that form the pelvic region of the human skeleton. Its lower part is somewhat thickened and is called the body of the PC, which forms the upper part of the acetabulum. The sacrum and femur bones are connected to the body of the ilium. During puberty, the PC fuses with the pubis and in the region, thus forming the pelvic bone.
On the inside of the body there is a line in the shape of an arc, and above there is a wide part of the bone called the wing of the PC, the lower part of which is narrowed and the upper part is widened. The edge of the wing is thickened, the abdominal muscles are attached to it, traces of which are imprinted on the bone in the form of three lines (lips): outer, inner and intermediate. It should be noted that the upper parts of the wings are called the iliac crests. The ridge is S-shaped and ends in front of the anterior superior PC, which can be felt on the human body through the skin, and in the back - with the posterior superior iliac bone.
Note that the anterior edge of the ilium fuses with and the posterior edge borders on the sciatic notch. The outer part of the wing is the attachment point for the gluteal muscles, and on the inner part of the wing, called the iliac fossa, there is an articular auricular surface, which is the point of connection with the surface of the sacrum. Above it is the iliac tuberosity, which serves to attach the ligaments.
The iliac fossa is the attachment point for the iliacus muscle. It is adjacent to the lumbar muscle and originates from the upper part of the fossa, the inner lip of the crest and the anterior sacral and lumbar ligaments. Together with the psoas major muscle, the iliacus muscle participates in the formation muscle mass walls abdominal cavity(back). Its functions also include hip flexion.
So, upper part The PC is rounded, the front and back form two protrusions each, and the outer part is somewhat elevated. In general, the relief of the bone depends on the muscles, in the places of attachment of which various lines, ridges, pits and spines have formed.
Thus, the ilium is one of three components that form a single pelvic bone. In humans, it connects to the sacral bone (fusion of five vertebrae) and in the area of the acetabulum fuses with the other two components of the pelvis. Muscles are attached to this area, in particular the iliopsoas, which, due to its contractions, forces the limb to move forward, that is, it controls their movement, and also stabilizes the pelvis, flexes the hip and lumbar spine.
To summarize, it should be noted once again that the ilium, whose function is to attach muscles, is involved in the process of formation and control of movements lower limbs. Connected to the joints and moved by the muscles, the PC also forms protection for the soft parts of the body, while at the same time allowing it to move smoothly. In addition, being part of the human skeleton, the ilium serves as a frame to which other limbs are attached, namely the lower limbs.
As the well-known saying goes: “If I knew where you would fall, I would spread some straw.” But unfortunately, we can never know what will happen to us in the next minute.
The human skeleton is a fairly strong frame, but with age our body loses many useful microelements, and our bones become very fragile and brittle. Therefore, despite the fact that the ilium is one of the largest bones in the human skeleton, even with a normal fall, its fracture is a very common occurrence.
Structure of the ilium
The ilium is located in the pelvic region. This is a paired bone, which consists of a right and a left bone, their structure is absolutely identical. In turn, each of these bones has its own body and wing.The body of the iliac bone is a thickened small section, which, with the help of muscles, smoothly merges with the bones of the pubis and ischium. In this case, the acetabulum is formed and the base of the pelvic bone is formed. The wing is formed from an expanded upper part, which in the form of an arc runs along the inner side, and the abdominal muscles are attached to the very edge of the wing.
Thus, the ilium is the basis of the pelvic bone. It is responsible for the attachment of muscles, controls the movements of the lower extremities due to muscle contractions, participates in the motor activity of the lumbar region and ensures smooth movements. In addition to all this, the ilium is the frame for all other parts of the body.
Causes and symptoms of iliac bone fracture
Fractures of the ilium in adults occur after a direct blow or strong compression of the pelvis, as well as after accidents or falls from a height; even athletes can experience a fracture of the iliac bone due to high physical activity (running). As for children, such an unpleasant incident can occur even as a result of contraction of the sciatic muscles.Fractures of the iliac bone can be either a closed type, where the surface of the skin remains intact, or an open type, where numerous lacerations appear on the skin. The causes of a fracture can be external factors (trauma) or pathology (bone weakness due to another hidden disease, for example, osteoporosis).
Main symptoms of a fracture:
Acute and sharp pain when moving one limb;Severe swelling at the suspected fracture site;
Impaired functioning of the limbs (in case of a fracture of the left iliac bone - the left leg, and vice versa);
Shortening of one of the limbs;
Loss of sensation in the buttocks.
In addition to the main symptoms, you should definitely pay attention to the hematoma, which, if fractured, will spread over the entire upper third of the thigh, since significant hemorrhage occurs in the area of the fracture. This is fraught fatal, since generally in such cases a person loses up to 3 liters of blood and damage to internal organs cannot be ruled out.
If you still suspect a fracture, call immediately ambulance and hospitalize the patient. Now he is provided with inpatient treatment for a month. If you are planning to transport such a patient yourself, then keep in mind following points. The position of the patient during transportation is strictly lying on his back, and a bolster must be placed under his knees. To detect a fracture, you only need to take a regular x-ray.
Remember! Never attempt to apply a splint yourself. This must be performed under anesthesia and by an experienced specialist. And since the fracture may also be displaced, the patient will definitely require surgical intervention. Where the main task for the surgeon will be to compare all the fragments.