The article presents the results of treatment of impression-compression fractures of the tibial condyles using a clinically substantiated method and device developed by the authors for repositioning the articular surface. Excellent and good results were obtained in 88.6% of cases, which is 1.2 times higher than previously reported data in the specialized literature.
Our experience of treating impressional fractures condyles of the tibia
Results of treatment of impression-compressional fractures of condyles of the tibia with application the developed authors, clinically reasonable method and apparatus for repositioning of the articular surface are presented. Excellent and good results were obtained in 88.6% of cases, which is 1.2 times higher than previously reported data in the special literature.
Area fractures knee joint refer to severe fractures of the bones of the limb. The frequency of such fractures, according to various authors, ranges from 4 to 6.1% of all fractures of the lower extremities. The peculiarities of fractures of this localization include the location of the fracture plane inside the joint, often accompanied by damage to the soft tissue elements. Violation of the congruence of the articular surfaces that make up the knee joint aggravates the nature of the damage and the course of the recovery process. The fusion of fractures in the area of the knee joint often occurs with the formation of excess regenerate tissue, which leads to joint deformity and a violation of the congruence of the articular surfaces, and is the cause of the development of stiffness and deforming arthrosis of the joint. The presence of intra-articular hematomas contributes to the formation of adhesions and scarring, which can be the cause of persistent contractures of the knee joint. The complexity of fractures in the area of the knee joint determines the difficulty of repositioning and ensuring adequate stable fixation of fragments for the period of fusion.
Most authors point to a significantly higher incidence of tibial condyle fractures compared to femoral condyle fractures. According to O.V. Oganesyan (2005, 2008), fractures of the proximal articular end (condyles) of the tibia account for up to 7.0% of all skeletal fractures. The tibial condyles are less resistant to violence than the femoral condyles, due to the anatomical features of the femoral and tibial metaepiphysis.
A characteristic feature of most fractures of the tibial condyles is the formation at the time of injury of a primary defect in the cancellous bone of the condyles, otherwise, the zone of primary indentation of the articular surface of the bone plateau, which in most classifications is defined as impression-compression fractures.
Treatment of fractures of the knee joint is a difficult task. Various complications and unsatisfactory outcomes of treatment, according to various authors, account for about 50.0%. The operative method is the main one in the treatment of compression-impression fractures of the knee joint area.
Since the mid-60s - early 70s of the last century, the method of transosseous osteosynthesis with external fixation devices has been successfully developed in our country, and, first of all, the method of G.A. Ilizarov, which has become the most optimal, including for the treatment of fractures of the knee joint. The advantages of the transosseous osteosynthesis method are as follows: firstly, the Ilizarov apparatus makes it possible to achieve an accurate reposition with the elimination of all types of displacements and with minimal tissue trauma without disturbing blood circulation in the damaged limb segment; secondly, it provides controlled osteosynthesis with the possibility of correcting the position of fragments during treatment. Stable fixation of fragments in the apparatus does not exclude in many cases the load of the injured limb and the possibility of early movements in the joints, which is a prevention of the development of contractures of the joints of the lower extremities. Methods developed at the RRC "VTO" named after Academician G.A. Ilizarov, made it possible to further improve the method of transosseous osteosynthesis.
At the same time, the developed classical methods of osteosynthesis with the Ilizarov apparatus are not without some drawbacks, primarily the inability to use it in the treatment of compression-impression fractures of the tibial condyles, which is associated with its constructive abilities. Within the walls of the Research Center "WTO" the method of CHKOS was further developed. Original layouts of rod and pin-rod external fixation devices based on the Ilizarov apparatus have been developed and successfully used in clinical practice, which made it possible to improve the outcomes of treatment of fractures of the knee joint, including compression-impression ones.
However, the problem of treatment of fractures of the knee joint cannot be considered completely solved. In this regard, we have made an attempt to improve the results of the treatment of fractures of the knee joint by improving the methods of treatment and creating clinically valid methods and devices.
In the Department of Emergency Traumatology of the National Research Clinical Center "VIO", 45 patients with compression-impression fractures of the tibial condyles aged 20 to 70 years were treated. The structure of fractures according to the mechanism of damage is represented by simple fractures of the internal and external condyles from depression - 17 (38%) and 20 (44%). In 8 cases (18%) fractures of both condyles were observed. For the treatment of this group of patients, the method of transosseous osteosynthesis was chosen using a device developed by us that provides congruence and restoration of the articular surfaces of the bones of the knee joint (RF patent for utility model No. 98896).
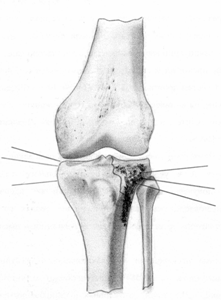
The task was achieved due to the fact that in the device for repositioning the articular surface, containing a hollow cylindrical body with a cutting edge and a pusher placed inside it with the possibility of longitudinal movement, the diameter of the pusher corresponds to the inner diameter of the body. The pusher is equipped with a locking head, while the body is equipped with a removable support in the form of a cylindrical rod, at one end of which there is an annular groove with a split ring placed in it, and at the other end - a cylindrical head with a handle perpendicularly installed in it (Fig. 1)
.
Figure 1. Device for repositioning the articular surface:
a) a diagram; b) appearance devices (Patent for utility model of the Russian Federation No. 98896)

b)
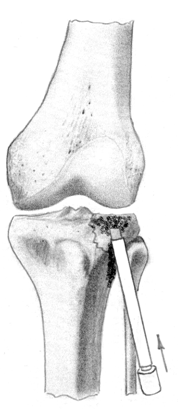
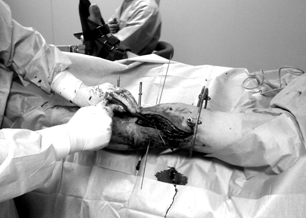
The device was used as follows (Fig. 2 a, b, c): after preparing the surgical field, an operative approach is performed: an incision is made along the anteroexternal surface of the damaged tibial condyle, exposing the proximal epimetaphysis of the tibia with a raspator.
Figure 2 (a, b, c). Method and device for repositioning the articular surface (Patent for utility model No. 98896)
but)
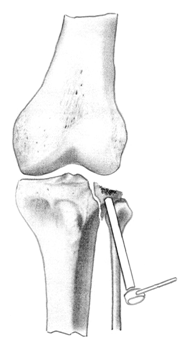 b)
b)
in)
In the paracapsular zone, the anterior section of the meniscus is cut off, which is sutured after osteosynthesis. A removable support is installed in the body of the device. Visual inspection of the fracture .
From the extra-articular side of the condyle, the device is installed in the direction towards the conditional center of indentation. Holding the device by the handle, strike with a hammer on the fixing head of the support, moving the device to the desired level . After deepening the body into the condyle to the required depth, the support is removed from the cylindrical hollow body and replaced with a pusher. The pusher is advanced along the cylindrical hollow body, manually or with a hammer, thereby advancing the bone cylinder inside the body to the level of the articular surface of the condyle.
Reposition control is carried out visually. The device is removed from the operational area. The defect of the bone substance of the condyle from below is filled with an autograft or osteoinductive material and fixed with pins in the support of the external fixation apparatus. The wound is sutured according to general surgical rules, drained.
An analysis of the treatment outcomes of patients with compression-impression fractures of the tibial condyles indicates the relative majority of excellent and good treatment outcomes when using the method of transosseous osteosynthesis with external fixation devices developed by us - 88.6% of the total number, which is 1.2 times higher, according to the data published earlier than the number of positive outcomes in the application of the classical layouts of the Ilizarov apparatus.
Let's give a clinical example
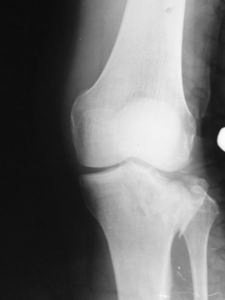
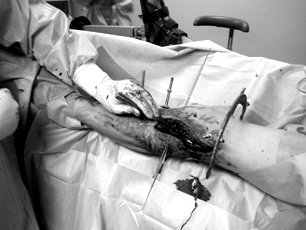
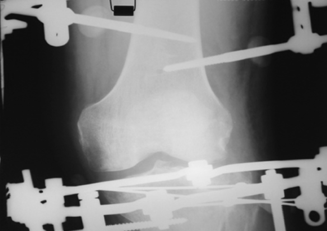
Patient G., born in 1973, was treated in the Department of Traumatology No. 1 of the GAUZ RCH of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Tatarstan from 10/19/11 to 11/23/11. As a driver of a car, he got into an accident. Delivered to the emergency room by ambulance. Diagnosis: closed compression-impression fracture of the lateral condyle of the left tibia. On October 26, 2011, an operation was performed - open transosseous osteosynthesis with an external fixation apparatus for an impression-compression fracture of the lateral condyle of the left tibia. Reposition of the condyle was performed using a device developed by us (Fig. 3 a-d). After achieving reposition, an external fixation device was mounted.
Figure 3. Patient G., born in 1973 Diagnosis: closed compression-impression fracture of the lateral condyle of the left tibia: a) radiograph before surgery: b, c - stage of surgery, d - during treatment
 but)
but)
 b)
b)
 in)
in)
 G)
G)
Thus, the use of the method and device developed by us for the treatment of impression-compression fractures of the knee joint area made it possible to achieve both accurate reposition with the elimination of all types of displacements and restoration of the anatomy of the damaged limb segment, and in the vast majority of cases, stable fixation of the proximal articular end of the tibia on growth period. The technology we have developed makes it possible to restore the congruence of the articular surfaces of the knee joint, which in turn dramatically reduces the development of gonarthrosis and disability.
H.Z. Gafarov, A.L. Emelin
Kazan State Medical Academy
Gafarov Khaidar Zainullovich - doctor medical sciences, Professor, Head of the Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics
Literature:
1. Balakina V.S. Intra-articular fractures of the knee bones / V.S. Balakin; LITO them. R.R. Vreden: V.G. Weinstein (responsible editor) and others // Intra-articular fractures: - L. Medgiz, 1958. - P. 138-179.
2. Gorodnichenko A.I. Treatment of near- and intra-articular fractures of the knee joint with apparatus / A.I. Gorodnichenko // New technologies in medicine. - Kurgan, 2000. - Part 1. - S. 62-63.
3. Kaplunov O.A. Transosseous osteosynthesis according to Ilizarov in traumatology and orthopedics / O.A. Kaplunov. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2002. - S. 62-78.
4. Linnik S.A. Indications and methods of treatment of patients with fractures of the condyles of the knee joint / S.A. Linnik, A.M. Khlynov, K.A. Novoselov et al. // Bulletin of the All-Union Guild of Orthopedic Prosthetists. - Spec. release. St. Petersburg, 2009. - S. 34.
5. Nigmatullin N.K. Transosseous osteosynthesis in the treatment of fractures in the knee joint / K.K. Nigmatullin // The Genius of Orthopedics, 1996. - No. 1. - S. 71-73.
6. Noskov V.K. Treatment of patients with fractures of the condyles of the bones of the knee joint with the Ilizarov apparatus / V.K. Noskov // Orthopedic, traumatology, 1988. - No. 9. - S. 26-28.
7. Oganesyan O.V. Treatment of chronic fractures of the condyles of the tibia using a hinge-distraction apparatus / O.V. Oganesyan // Vestnik traumatol. and an orthopedist. them. N.N. Priorova, 2005. - No. 2. - S. 53-56.
8. Plotkin G.L. The problem of impression fractures of the condyles of the tibia / G.L. Plotkin, V.P. Moskalev, A.A. Domashenko and others // Bulletin of the All-Union Guild of Orthopedic Prosthetists. - Spec. release. St. Petersburg, 2009. - S. 52.
9. Khlynov A.M. Causes of intra-articular fractures of the condyles of the knee joint / A.M. Khlynov, E.G. Lapshinov, F.V. Artemiev and others // Bulletin of the All-Union Guild of Prosthetists-Orthopedists. - Spec. release. St. Petersburg, 2009. - S. 69.
10. Shelukhin N.I. Treatment of intra-articular fractures of the condyles of the femur and tibia different ways/ N.I. Shelukhin // Ambulatory surgery: Russian quarterly scientific and practical. Journal. - St. Petersburg: CJSC Rosmedium - North-West, 2004. - No. 1/2. - S. 37-38.
Severe is the fracture of the condyle. The treatment of this disease is quite
long process, which should be treated with patience and all seriousness. After the situation is corrected, the patient will also have a rehabilitation period.
Mechanisms of fractures
Most often in medical practice there is a combined version of such an injury. The cause of a condyle fracture can be:
- A direct blow with a hard object directly to the knee.
- Fall with a landing on the knee joint, even if it is in a bent state;
- A blow that is provoked by a fall from a great height onto straight legs.
Kinds
Today in medicine there are various classifications of fractures of the condyle of the knee joint.
There is an option with an offset, without an offset. However, more and more often they resort to the classification developed by Novachenko. He highlights:
- Fracture of 2 condyles with displacement. This is possible if the force acts on the joints strictly vertically;
- Fracture of the condyle of the tibia. In this case, no displacement occurs;
- Fracture of one condyle with displacement;
- Fracture with subluxation of the leg. In this case, one or both condyles may be affected. In this case, it is noticeable even outwardly that the lower leg is deflected either outward or inward.
Symptoms or how to recognize an injury
To understand that a fracture of the knee joint has occurred, the symptoms that appear almost immediately after the injury will help:
- First, there are severe pains that are localized in the knee and thigh;
- The outlines of the knee joint acquire a smoothed shape, because. hemarthrosis occurs;
- The patella is unstable, "floats", ballots;
- There is a feeling of wobble (i.e., there is a feeling that the knee is oscillating);
- When the knee joint is felt by a specialist, when there is pressure on the condyle, a sharp pain occurs;
- When the condyles are displaced, the following position of the lower leg appears: it is either laid back or brought inward;
- In some cases, shortening of the lower extremities is observed;
- Another symptom is that movements in the knee joint are quite painful, a characteristic crunch appears.
Despite the fracture, the victims can move around and, if necessary, even raise their legs. This is due to the tension of the femoral muscles.
Of course, at the first manifestations of an injury, if symptoms and suspicions of a fracture arise, you should consult a doctor. Only the right treatment will help restore the health and normal functioning of the knee joint.
Methods for determining a fracture by a doctor
It is not easy to understand that the patient has a fracture of the condyle of the knee. After all, it is necessary to distinguish it from many other injuries that have similar symptoms:
- contusion, but with it the pressure directly on the condyles is absolutely painless. This is checked during inspection;
- ligament rupture, but at the same time, the lower leg does not deviate to the side, and when it is moved by a doctor, it subsequently returns to its normal position;
- stretching;
- fracture of the tibia or patella. However, in this case, the pain center is located either above or below the knee joint.
In addition to an external examination by a doctor, in order to determine the diagnosis, an x-ray is required. It is the results of this diagnostic study that are of decisive importance.
How to treat fractures without displacement
Immediately after a condyle injury, the first step is to remove all the blood that has accumulated there from the knee joint. This happens with the help of a puncture. After the procedure, the needle is not removed. Through it, a small amount (20 ml) of a 2% novocaine solution is injected into the joint. Then, when the hematoma is removed, it is necessary to apply a plaster cast:
- it should be with a window directly above the joint from the buttock to the very tips of the fingers, if it is a fracture of the condyles of the tibia;
- hip bandage, if observed.
When applying a cast, you need to ensure that the knee joint is bent by about 5-7 degrees.
Literally on the 2nd day, it is recommended to train the quadriceps muscle. The exercise consists in lifting the leg, which is enclosed in a plaster cast. In this case, the patient is at rest all the time, bed rest is prescribed.
Only after a week you can start moving on crutches. In this case, there should be no load on the knee joints. Only after 6-10 weeks the plaster will be removed. After that, it will be necessary to actively and regularly engage in therapeutic exercises.
It is possible to give the joint a load only a few months after the treatment of the fracture has begun. Otherwise, there is a possibility that the broken condyle will settle, and the vessel will deform. All this in general will lead to arthrosis of the knee joint.
If there was a displacement during a fracture: how to treat
Treatment of a displaced condyle fracture is carried out in several ways. It all depends on the severity of the injury. Most often, conservative treatment is carried out. And only in rare cases is surgical intervention prescribed.
Option 1. Conservative approach
The treatment of a displaced condyle fracture must adhere to one basic rule. The condyle must be moved to the correct level until it is in the correct position. And only then the joint is fixed exactly for the period that is necessary for fusion. Reduction occurs with anesthesia as follows:
- if the internal condyle is damaged, slightly move the lower leg outward;
- if the external condyle is damaged, the lower leg is retracted inward.
On the second day after the plaster is applied, you can do exercises. This will be the leg lift, the initial rehab. Only after 28 days can you start walking on crutches. At the 10th week, the bandage is removed. A full-fledged load on the knee joint is possible only 3 months after the fracture.
Option 2. Constant traction
If the doctor decides to carry out the method of constant traction, then the puncture can be performed not immediately after the injury to the joint, but on the 4th day. This method has an important advantage. When using it, the knee joint is always in the open position. Therefore, if necessary, you can always make a puncture.
injured lower limb without fail placed in a special tire. In this case, the knee joint must be bent 10 degrees. A needle is passed through the calcaneus, a load of 5 kg is suspended on it. Literally after 2 days, lateral thrusts are also applied to the flannel bandage:
- One is located in the region of the condyle;
- The second is at the bottom of the leg.
A load of 3 kg is suspended on both rods. This may be enough to correctly set the affected condyle.
After 5 weeks, if a good comparison has occurred, a cast is applied to the leg. In the future, the treatment provided for the usual fracture of the condyle is carried out.
Option 3. Operation
If all conservative methods have not been successful, the doctor must prescribe treatment in the form of surgical intervention. The operation is scheduled for the period from 3 to 5 days after the injury. The intervention is performed under anesthesia. After the operation, a plaster is applied to the knee joint, leaving a window. Through it, after a week or a little more, the stitches are removed. After that, the window is also plastered. Further rehabilitation occurs, as in the case of a fracture without displacement.
If a metal bolt was placed during the operation, it is removed after 8 months. In the case when the patient has a fracture of both condyles, the operation is performed on both legs at once. And correctly set condyles are fixed with bolts, which are then removed during the next surgical intervention under anesthesia. Proper fusion of the knee joint with a fracture of the condyle takes a long time. At the same time, there should not be any load on it. Otherwise, re-shifting may occur. Therefore, you need to be extremely careful. A full load on the damaged joint is allowed only after 4 months of rehabilitation after injury.
rehabilitation period
Recovery after such a serious fracture is a series of necessary measures:
- exercise therapy. Always with inactivity of the muscles, their atrophy, impaired walking and mobility of the joint itself are observed. In order for rehabilitation to go well after an injury, you need to adhere to a set of exercises. All of them should be done regularly and constantly. For their implementation, special equipment is used. Exercises are performed under the supervision of a professional instructor. And only a specialist prescribes specific types of exercises.
- Massage. Rehabilitation includes the appointment of a massage. It helps to improve the blood supply to the affected muscles and tissues, stimulates the restoration of elasticity and muscle tone, as well as the entire muscle mass as a whole.
- The third component of the rehabilitation period is physiotherapy. Its main goal is to save the patient from tissue edema, from the pain that accompanies throughout the entire recovery period. Physiotherapy procedures will also help reduce the risk of developing post-traumatic arthrosis of the joints. (voted: 32 , grade: 4,22 out of 5)
Attention! Did you notice a mistake in the text? Select it with the mouse and press the keys in sequence Ctrl+Enter. Thanks for helping us develop the site!
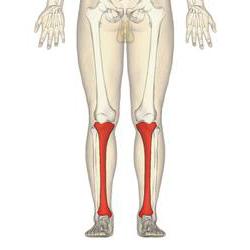
The tibia is one of the key bones in the human body. It is extremely large and is located medially compared to the lower leg bone. In its upper part, it connects to the femur. Thus, the knee joint is eventually formed. In the lower part it adjoins the talus.
Body of the tibia
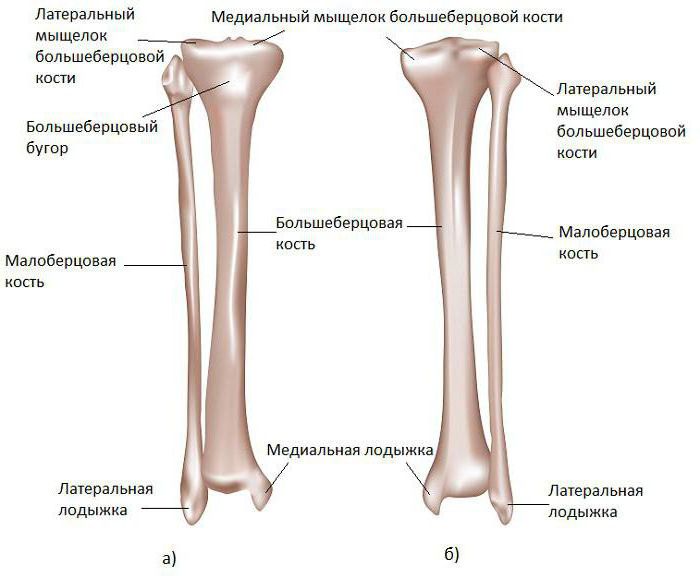
The tibia is a regular trihedron with three distinct edges.
The first edge is the front. It can be felt through the skin and, if desired, palpated. In its upper part there is a characteristic tuberosity. It is in this place that the quadriceps femoris muscle joins the tibialis.
The second edge is interosseous. It is somewhat deployed in the direction of the fibula. At the same time, it is very sharp.
The last, third, medial edge is also called the middle edge by physicians. It has a characteristic rounded shape.
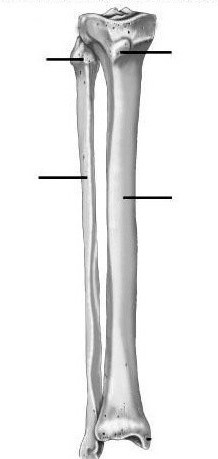
The structure of the tibia
At its end, the tibia forms a pair of thickenings that serve to attach muscles. In anatomy, they are called condyles. There are two of them in the tibia - lateral and medial.
On the side that is closer to the human thigh, the condyles are equipped with slightly concave platforms, which are necessary for connection with the same condyles of the femur. The articular surfaces of the condyles are separated by a kind of elevation, which has two tubercles. They are needed for reliable fastening of the articular ligaments.
Trauma to the posterior edge of the tibia
The posterior edge of the tibia is extremely susceptible to fractures and injuries. Injuries of this kind occur in a third of all victims of ankle fracture.
Most often, according to the experience of traumatologists, a bone fragment is located in the back, possibly on the lateral side of the surface. The connection of bone fragments after a fracture for their better fusion in the case of fractures of the tibia is carried out only when the size of the fragment does not exceed a quarter of the entire surface of the joint.
Doctors distinguish several types of damage to the posterior lateral edge of the tibia. Firstly, in the presence of a fragment of sufficient size, one speaks of a contour fracture of the posterior ligament.
Second, the condition of the fragments within the joint itself.
Thirdly, if the surface of the tibia itself is depressed during the fracture, then most often it is not possible to make an accurate diagnosis using only one initial x-ray. These are the most complex cases that require detailed and scrupulous study. Often, as a result of indentation, obstacles are formed, due to which it is not possible to quickly and effectively set the bone.
Right tibia
For clarity, consider what the tibia is. The right one, upon detailed examination, consists of 9 components.
At the heart of the intercondylar eminence. To the right and slightly below it is the medial condyle, and even lower and in the center is the tuberosity of the tibia.
An important component of the structure is the interosseous edge, under which the lateral surface is located, as well as the anterior edge, under which the medial surface is located.
The tibia ends with the medial malleolus. Anatomy today has carefully studied all the details of the structure of the human body, which today greatly simplifies the process of diagnosis and treatment.
Another component that cannot be ignored is the lateral condyle. It is located in the upper left side of the tibia.

Tibia by department
Considering the sections of the tibia, the main attention should be paid to the proximal section. It includes upper part bone that is directly involved in the formation of the knee joint. This department consists of two condyles. One is external, the second is internal, as well as the metaphysis. If during the damage the fracture line affected the articular surface of the tibia, then traumatologists call it articular.
Fractures of this part of the tibia can be mild (they are also called low-energy), for example, obtained by falling from a small height. And also more complex or high-energy ones, for example, with a strong mechanical blow to the knee area - during a football match or a collision with a car.
The second cases are more dangerous, because as a result of such injuries, the likelihood of a large number of bone fragments is high. In any case, a fracture of this bone clearly belongs to the category of severe injuries and requires professional and qualified treatment. Most often, you can not do without surgery to splice broken bones and shift the resulting fragments. In this case, the tibia is fastened with screws, sometimes plates are added to them.
If it is precisely established that the fracture is intra-articular, then it is very important in this case to thoroughly restore the damaged surface, eliminating the displacement of bone fragments.
Otherwise, it is fraught with complications, the most common is post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the knee joints.
Intercondylar eminence
Another severe injury occurs when the intercondylar eminence of the tibia suffers. Such injuries are extremely painful and unpleasant. Most often they occur under the influence of indirect mechanical trauma. For example, when the impact is from behind or in front of the proximal leg, which is in a bent position. As a result, the cruciate ligaments are stretched to the limit, and the bone is torn off. Another cause of such fractures is excessive abduction or hyperextension.
The first signs of just such damage are sharp pain and swelling in the area of the knee joint. As a rule, the injury is the cause. Often such injuries occur in athletes from contact sports. The patient cannot fully extend the leg, most have a drawer symptom. True, it is not always possible to install it due to spasm of the muscles that surround the knee joint. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, an x-ray is prescribed. Such fractures are often accompanied by damage to the lateral ligaments on the knee joint.
Fracture treatment
At the same time, they lend themselves effective treatment injuries in which the tibia is the main bone. Anatomy advises to set the main task of treating such a patient - restoring the stable operation of the joint, as well as establishing movement in it. A few days after the injury, it will not hurt to consult an orthopedic doctor who will give practical advice so that the recovery process goes optimally and quickly.
In the course of treatment, repositioning will most likely be required, which can be done in a closed way by applying a plaster cast in the position of the leg in which it is at full extension. The bandage should be worn for one and a half to two months.
If the fracture is accompanied by other injuries, then closed repositioning is best avoided.
In the case of a complete detachment of the ligaments, it is necessary to start surgical treatment as soon as possible. Such fractures are often accompanied by serious complications, severe pain, as well as unstable fixation of the knee joint.
Tibial ligament injury
The ligaments of the tibia are also subject to severe injury. The first symptom is a sharp pain on the inside of the knee that occurred immediately after the injury that caused the rupture. It is often difficult to identify one source of pain.
It is necessary to provide first aid as soon as possible. Immerse your foot in absolute rest. Apply ice to help relieve swelling and reduce pain. If needed, you can take a painkiller tablet.
Often occurs in conjunction with other significant injuries of the knee, such as injury to the external meniscus, damage to the collateral or anterior cruciate ligament.
Symptoms of a condyle fracture
The muscular system of the leg connects two large bones - the femur and tibia. The condyles are ball-shaped projections located at the bottom of the femur. The role of the condyles in the motor function of the leg is great. With the help of the condyles, flexion and extension of the joint occurs, and there is also the possibility of turning the leg bone outward and inward.
A tibial condyle fracture has the following symptoms:
- Substantial knee, completely blocking the movement of the leg. When you press on the knee, it is greatly enhanced.
- Significant enlargement of the knee joint.
- In some cases, there is a clear deformation and deviation of the lower leg to the side.
Diagnosis of a condyle fracture
Traumatologists confidently speak of a condyle fracture when it is displaced by more than 4 mm. A fracture is diagnosed after a thorough examination by a traumatologist and an X-ray examination. The pictures clearly show the severity and nature of the fracture.
Fracture treatment
A fracture of the condyles of the tibia is a fairly serious injury that requires mandatory hospitalization after first aid. Complete healing and recovery of the condyles occurs only 5-6 months after the injury.
Treatment for a condylar fracture depends on the presence of displacement. Non-displaced fractures are punctured to remove blood and fluid. Further, for the purpose of fixation, a plaster is applied to the entire leg from the buttocks to the toes.
When diagnosing a fracture with displacement, the traumatologist performs reposition and eliminates the displacement, after which skeletal traction is applied for up to 6 weeks. If there are many bone fragments, there is a need for surgical intervention, in which bone fragments are fastened with screws, knitting needles, staples or steel plates.
For any type of fracture, 4-6 weeks after the injury, it is strongly recommended to gradually increase the load on the joint. Doctors recommend physiotherapy exercises, in which the patient is under close supervision medical worker begins to move in the knee joint. The patient is also shown massage and thermal procedures.
- damage to the lateral sections of the upper part of the tibia. Refers to the number of intra-articular fractures, occurs with a direct blow, falling on the knee or on straightened legs. May be accompanied by displacement or depression of fragments. It is manifested by sharp pain, hemarthrosis, severe limitation of movements in the knee joint and impaired support. The diagnosis is clarified with the help of radiography, less often CT is used. Treatment tactics depend on the type of fracture, a plaster cast, skeletal traction and various surgical techniques can be used.
Symptoms and diagnosis of tibial condyle fractures
At the time of the injury, there is a sharp pain in the knee. The knee is enlarged in volume, with a fracture of the internal condyle, varus deformity can be detected, with a fracture of the external - valgus. Movement and support are sharply limited. Pathological mobility is observed during lateral movements in the joint. Gently pressing on the condyles with one finger, you can usually clearly define the zone of maximum pain. There is a pronounced hemarthrosis, which sometimes causes a sharp expansion of the joint and disturbances in local blood circulation.
The main method of instrumental diagnostics is radiography of the knee joint. X-rays performed in two projections. In the vast majority of cases, this will make it possible to reliably establish not only the fact of the presence of fractures, but also the nature of the displacement of fragments. With ambiguous results of radiography, the patient is referred for a CT scan of the knee joint. If concomitant damage to soft tissue structures (ligaments or meniscus) is suspected, an MRI of the knee joint is prescribed. Sometimes fractures of the condyles are accompanied by compression of the nerves and blood vessels, if damage to the neurovascular bundle is suspected (damage to the vessel and nerve damage), consultations of a vascular surgeon and a neurosurgeon are prescribed.
Treatment of fractures of the tibial condyles
Treatment of this pathology is carried out in the conditions of the trauma department. Upon admission, the traumatologist performs a puncture of the knee joint and injects novocaine into the joint to anesthetize the fracture. Further tactics are determined taking into account the characteristics of the damage. In case of incomplete fractures, cracks and marginal fractures without displacement, plaster is applied for 6-8 weeks, walking on crutches is prescribed, the patient is sent to UHF and exercise therapy. After the termination of immobilization, it is recommended to continue using crutches and not lean on the limb for 3 months from the moment of injury.





